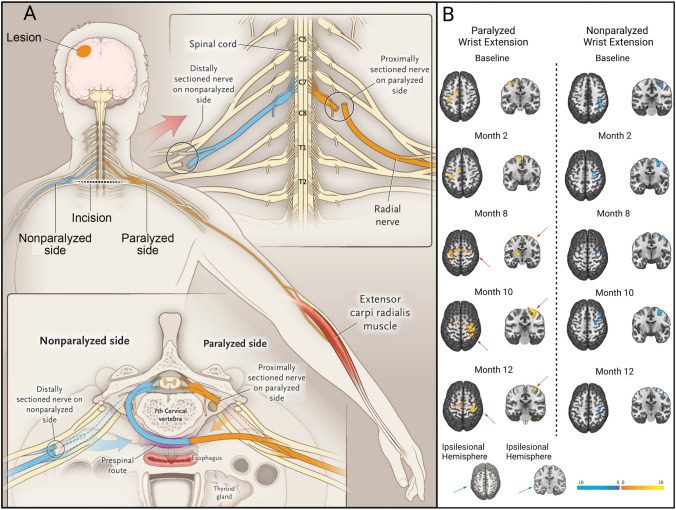
Fig. 4.
Crossing nerve transfer surgery to improve motor function by enhancing neuroplasticity in the contralesional hemisphere in patients with unilateral arm paralysis [41]. A Procedure of contralateral C7 nerve transfer surgery. After harvesting the bilateral C7 nerves in adequate sites, the C7 nerve on the non-paralyzed side (blue) is drawn behind the trachea and esophagus via a pre-spinal route to the paralyzed side (yellow) and coapted directly to the C7 nerve on the paralyzed side. B Functional MRI assessment in patients with CC7 surgery. The changes in brain activation on fMRI are evaluated during the 12 months after surgery. Left: Brain activation (yellow) during active extension of the paralyzed wrist. Before surgery, activation was only evident in the ipsilesional hemisphere. At month 8, activation began to appear in both hemispheres. Contralesional activation was enhanced and extended to a larger area than ipsilesional activation at 10 months after surgery, and it was weaker and covered a smaller region at month 12 than at month 10. Right: Brain activation (blue) during active extension of the non-paralyzed wrist. Brain activation associated with movements of the non-paralyzed wrist was stable in the contralesional hemisphere before and after surgery.