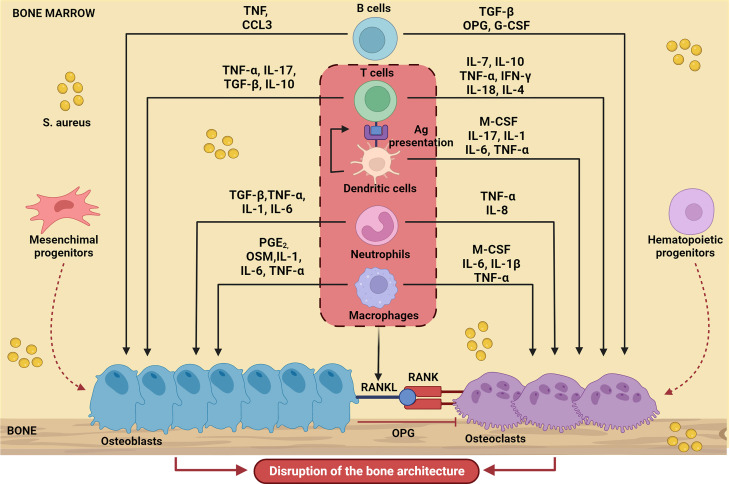
Figure 1.
Schematic representation of bone cell regulation by the main soluble factors produced by immune cells during S. aureus-induced osteomyelitis. Upon infection, immune cells migrate into the bone microenvironment and release cytokines (IL-17, IL-10, IL-1, IL-1β, IL-6, IL-7, IL-18, IL-4, IL-8), chemokines (CCL3), growth factors (M-CSF, G-CSF) and other several inflammatory mediators (TNF-α, PGE2, TGFβ, INF-γ, OSM) that influence osteoblast and osteoclast activity. The result is massive disruption of the normal bone architecture. The Figure was created with BioRender.com.