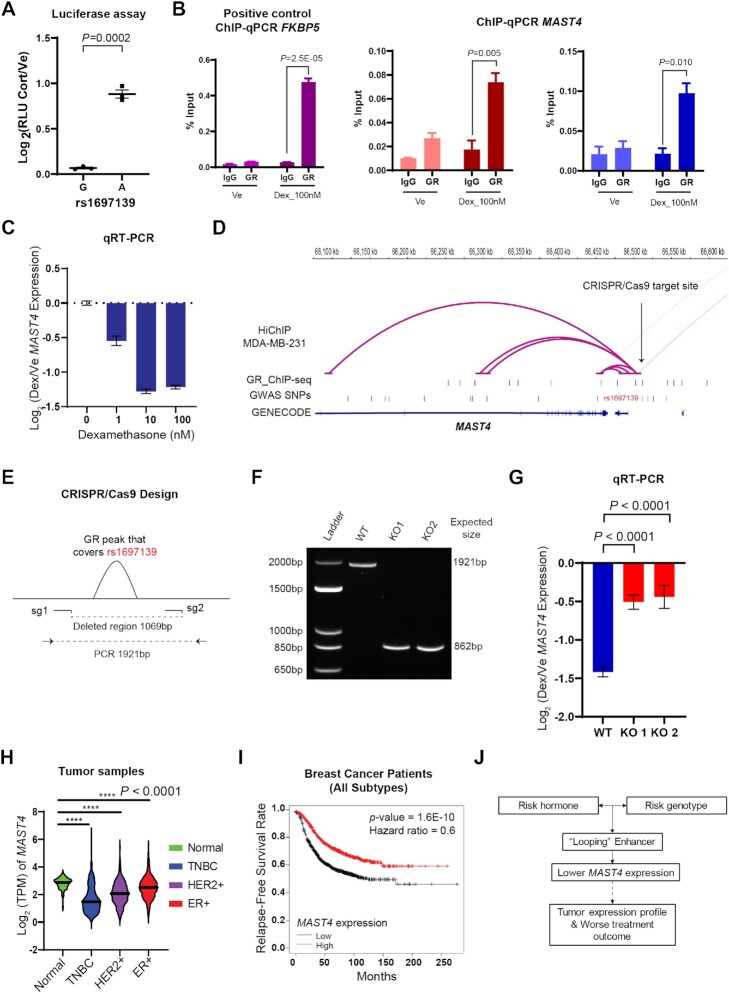
Figure 7.
Functional Validation of rs1697139-MAST4 GR-dependent PGx-eQTL in Breast Cancer Cells. (A) SNP-dependent and drug-dependent enhancer activity of the PGx locus associated with breast cancer in Figure 6 as measured by luciferase reporter gene assay in MDA-MB-231, a triple negative breast cancer cell line. RLU stands for relative light units and reflects normalization of luciferase signal to Renilla signal as an internal control. (B) ChIP-qPCR assays that tested GR binding at the PGx locus for MAST4 in MDA-MB-231 using two different primers. ChIP-qPCR targeting FKBP5 peak served as a positive control. P-values from Student's t-tests. (C) Dose-dependent repression of MAST4 by glucocorticoids in MDA-MB-231 cells. (D) Epigenomic datasets for MDA-MB-231 cells demonstrated that the SNP locus also looped to MAST4 in MDA-MB-231. GR ChIP-seq was downloaded from the database ReMap2022. (E) Designs of guide RNAs utilized in the CRISPR/Cas9 experiment that cut out the PGx SNP enhancer locus where GR binds and primers to test editing outcomes. (F) Gel electrophoresis of PCR products amplified with primers targeting the cut region demonstrated successful edits. (G) MAST4 gene expression as measured by qRT-PCR after CRISPR/Cas9 edits showed that the glucocorticoid-dependent repression was alleviated after the PGx SNP locus was cut out across two colonies of pure knock-out cells. Data included three biological replicates. (H) Expression of MAST4 in tumors from breast cancer patients in the TCGA database. **** P-values < 0.0001 by Student's t-tests. TPM stands for transcripts per million. (I) Kaplan–Meier curves for relapse-free survival rate in 1764 breast cancer patients predicted based on MAST4 expression. (J) Summary of functional insights gaining from in-depth studies of a GR-dependent eQTL and their implications for breast cancer risk.