Fig. 4. Set sizes across networks for ten sponge networks and randomizations of these networks.
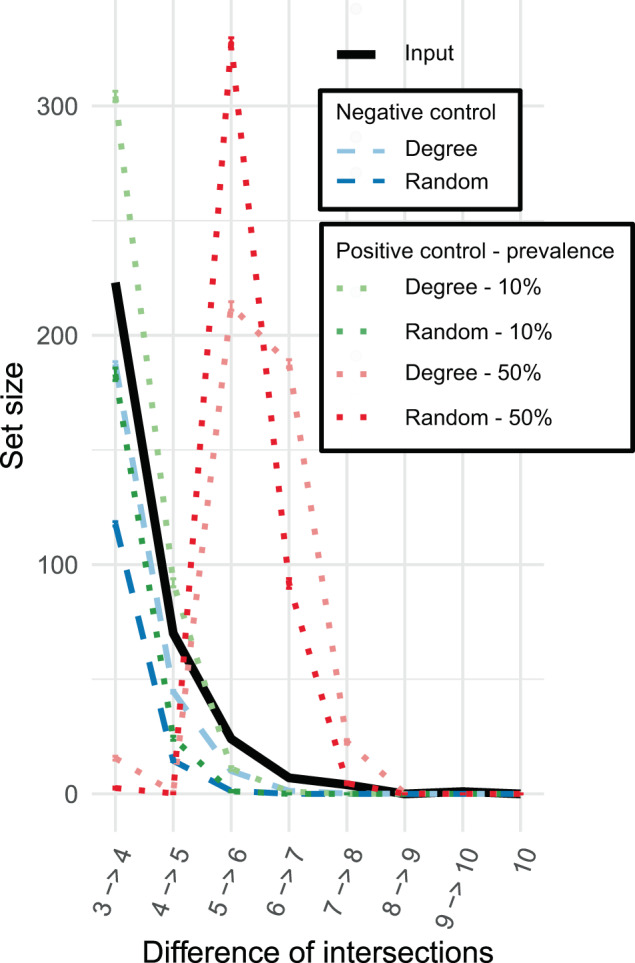
The set size is the number of edges present in a particular number of networks. The set size is shown for a set of sets of network intersections, meaning that the set of sets 4→6 is calculated as the number of edges in four or five networks with all edges in at least six networks removed. Each network was generated for a different host sponge order for which at least 50 samples were available. These networks were then randomized either with the same degree distribution (degree) or without this distribution (random). Moreover, each of the networks was randomized with preservation of a part of the input network for a subset of the randomizations as a positive control. Hence, the positive control degree networks are randomized versions of each input network with 20% of the union of associations present in at least 20% of observed networks or at least 50% of observed networks. Error bars represent the standard error across different combinations of random networks. For sets of edges present in up to six networks, the set size of the input networks deviates significantly from the set size from those of random networks with or without degree preservation.
