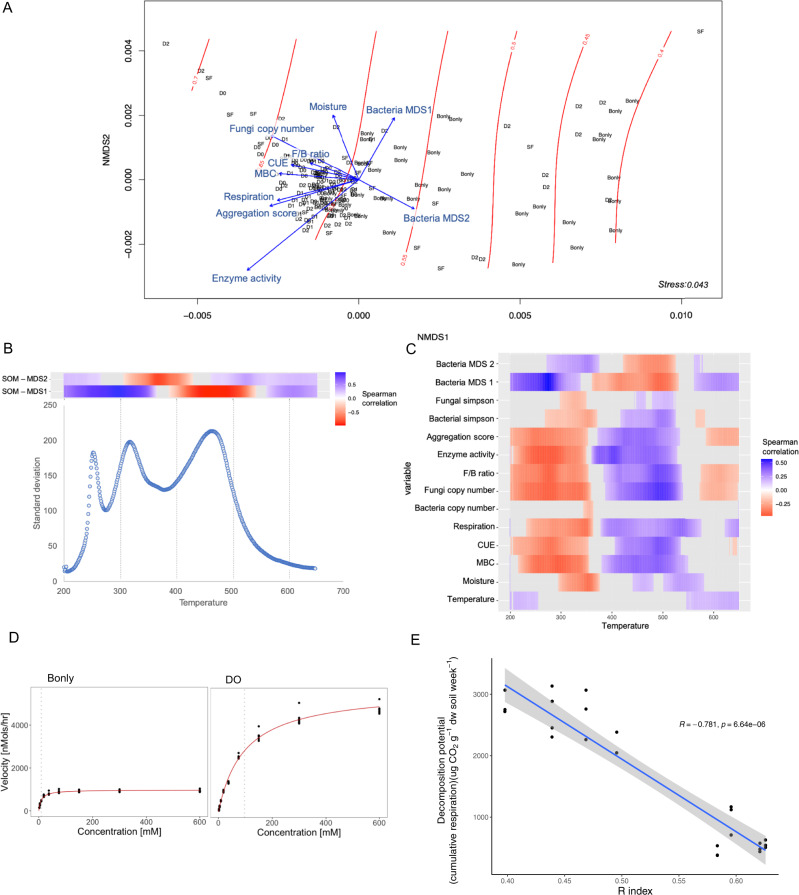
Fig. 1. Drivers of SOM composition and persistence.
Ordination of soil organic matter composition originated from a microbial diversity experiment in which a soil inoculum from a temperate forest was manipulated by consecutive dilutions (D0 > D1 > D2); selection of spore-forming microorganisms (SF); fungal exclusion (“Bonly”); inoculated into a model soil and grown on cellobiose as sole carbon source for 120 days under two temperatures (15 oC and 25 oC) and two moistures (30% and 60% WHC) in a full factorial design. Non-metric multidimensional scaling of Bray–Curtis distance from the pyrolyzed fraction of SOM based on Rock-Eval® analysis. Red contour lines represent the SOM thermal-stability R-index with higher numbers indicating more thermal-stable SOM. Significant explanatory variables (P < 0.05) are represented as blue vectors and the lengths of the arrows are proportional to the strength of the correlation; enzyme activity corresponds to the maximum activity recorded (Vmax g−1 dw soil); Bacteria MDS1 and MDS2 represent the first and second axis of the bacterial community structure, respectively; Fungal copy number and bacterial copy number correspond to the quantification by qPCR of ITS and 16 S rRNA gene (copy number g−1 dw soil); F/B ratio correspond to the fungal to bacterial ratio abundance; CUE represents the carbon use efficiency; MBC corresponds to microbial biomass carbon (µg C g−1 dw soil); Respiration represents the cumulative respiration measured during microcosms incubation (C-CO2 g-1 dw soil) and aggregation score represents the water stable aggregate formation at the end of incubation (A). Spearman correlation between the SOM ordinations axes points and the FID signal captured at different temperatures and standard deviation of signal across all microcosms by temperature (B). Spearman correlation between biotic variables and abiotic experimental treatment conditions and the FID signal captured at each temperature (C). Betaglucosidase enzymatic kinetics at representative samples for “Bonly” and D0 treatments, vertical line represents the Km (D). The relationship between thermal-stability R-index and decomposition potential measured in a follow-up experiment in which soil generated during the 120 days of incubation was inoculated with another community and cumulative respiration measured as a proxy for decomposition potential of microbial-derived SOM (E).