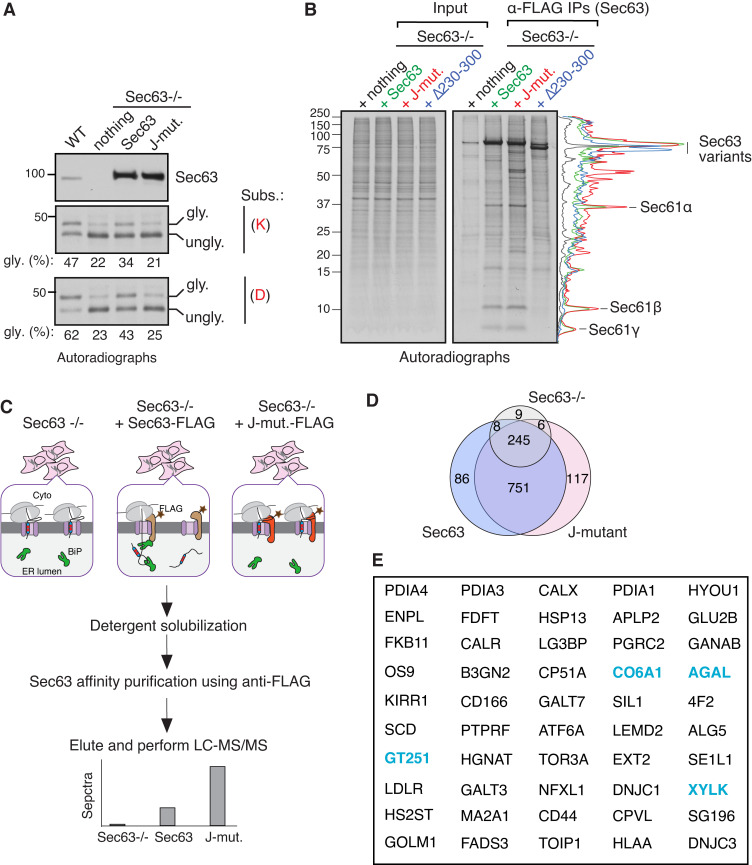
Figure 2.
Identification of endogenous Sec63 substrates retained at the Sec61 translocon. (A) WT HEK293 or Sec63−/− cells stably expressing the indicated Sec63 constructs were transfected with the C-TMD of WRB substrate carrying either lysine (K) or aspartic acid (D). The transfected cells were radiolabeled and analyzed by autoradiography after IP with anti-GFP antibodies for substrates. The immunoblot shows the expression of Sec63 from the indicated cell lines. (B) The indicated Sec63−/− complemented cell lines were radiolabeled and analyzed by autoradiography after IP with anti-FLAG beads. The traces are densitometry profiles of lanes and are shown on the right side of the autoradiograph, illustrating a selective enrichment of signals with the Sec63 J-mutant (HPD/AAA). (C) A scheme describing affinity purification and identification of translocon-occupied substrates by MS. (D) Venn diagram of protein distribution among the three groups of MS data from Table S1. Candidate proteins of 117 were at least twofold enriched in Sec63 J-mutant relative to WT Sec63 and fivefold increased than Sec63−/− cells. Candidate proteins of 86 were at least twofold enriched in WT Sec63 compared to Sec63 J-mutant and fivefold increased than Sec63−/− cells. (E) The top 50 secretory and membrane proteins from Table S2 that were enriched in Sec63 J-mutant. The blue color labeled proteins were previously identified in the study by Schorr et al. (2020). Source data are available for this figure: SourceData F2.