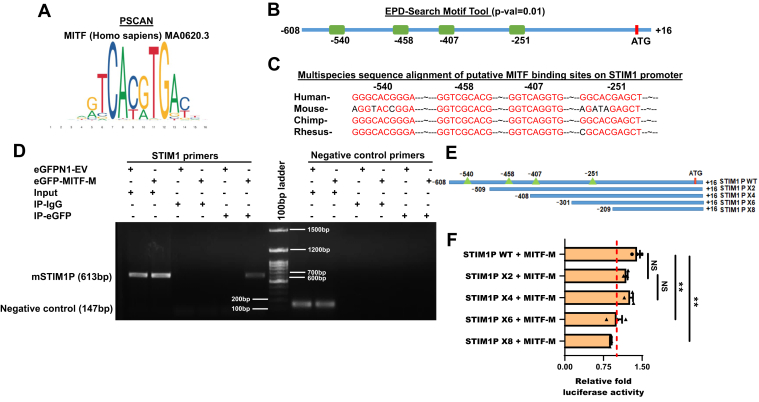
Figure 5.
MITF binds on STIM1 promoter and regulate STIM1 promoter activity.A, position weight matrix for human MITF consensus binding sequence. B, identification of putative MITF-binding sites on the STIM1 promoter using the EPD-Search Motif Tool at p-val cut-off of 0.01. C, bioinformatic characterization of conserved MITF-binding sites on the cross species alignment of the STIM1 promoter using the ContraV3 transcription factor binding analysis tool. D, chromatin immunoprecipitation assay in B16 cells with overexpression of eGFP-MITF-M or vector control. Crosslinked and sonicated chromatin from both conditions was immunoprecipitated using specific GFP antibody or control IgG. Immunoprecipitated DNA was amplified using primers specific to either mouse STIM1 promoter aligned to human STIM1 promoter or negative control region. PCR products were visualized on agarose gel (N = 3). E, the cartoon representing potential MITF-binding sites in WT hSTIM1 promoter and different truncations in hSTIM1 promoter (green triangles represent four putative MITF-binding sites within the 624bp-cloned region of the STIM1 promoter and red bar represent ATG start site). F, normalized luciferase activity of WT STIM1 promoter and different truncated STIM1 promoters upon overexpression of MITF-M in B16 cells (N = 3). Data presented are mean ± S.E.M. One-way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s post hoc test was performed for panel F. F and p values for panel F are F = 11.10 and p = 0.0011, respectively. Here, NS means nonsignificant and ∗∗p < 0.01. EPD, Eukaryotic Proteome Database; MITF, Microphthalmia-associated transcription factor; STIM1, Stromal Interaction Molecule1.