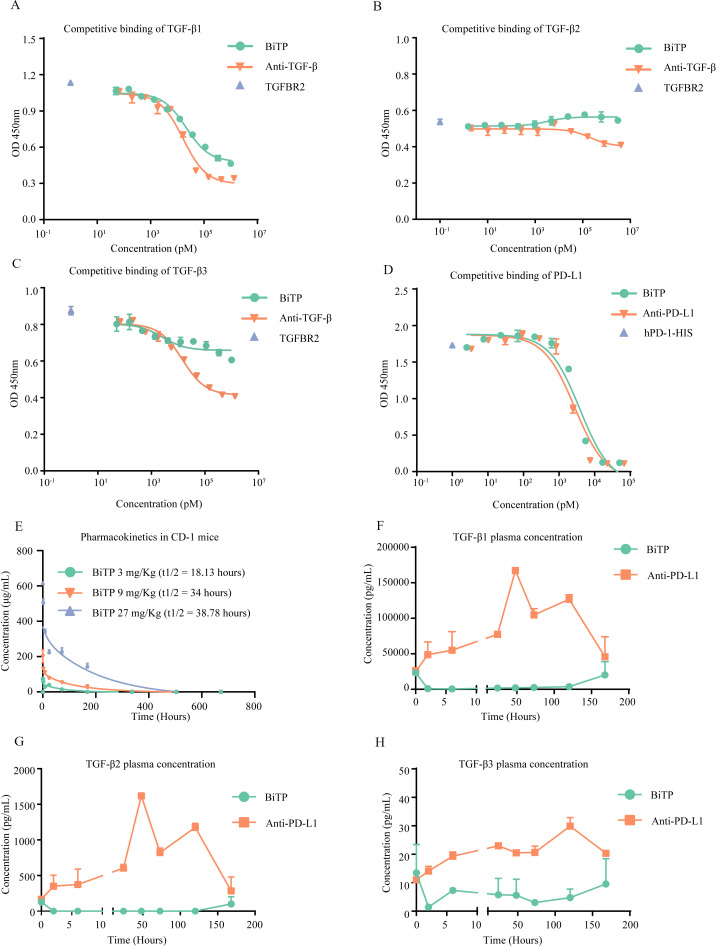
Figure 2.
Competitive binding experiments and pharmacokinetic study. (A–C) BiTP competitively inhibited the binding of TGFBR2 to TGF-β. TGFBR2-HIS and BiTP were incubated with precoated TGF-β. The competitive inhibition capability was evaluated with anti-HIS ELISA. (D) BiTP competitively inhibited the binding of PD-1 to PD-L1. PD-L1-HIS and BiTP were incubated with precoated PD-L1. The competitive inhibition capability was evaluated with anti-HIS ELISA. (E) CD-1 mice received 3 mg/kg, 9 mg/kg, 27 mg/kg BiTP treatment by intravenous injection. Then, 5 min, 2 hours, 8 hours, 24 hours, 3 days, 7 days, 14 days, 21 days, and 28 days later, 0.6 mL peripheral blood was collected to measure the concentration of BiTP in plasma. (F–H) The influence of BiTP on the concentration of TGF-β in plasma. B-cell-depleted (μMT) mice received 9 mg/kg BiTP and 6.6 mg/kg anti-PD-L1 treatment. Before treatment, as well as 2 hours, 6 hours, 24 hours, 24 hours, 72 hours, 120 hours, and 168 hours after treatment, peripheral blood was collected to measure the concentration of TGF-β. TGF-β, transforming growth factor-beta.