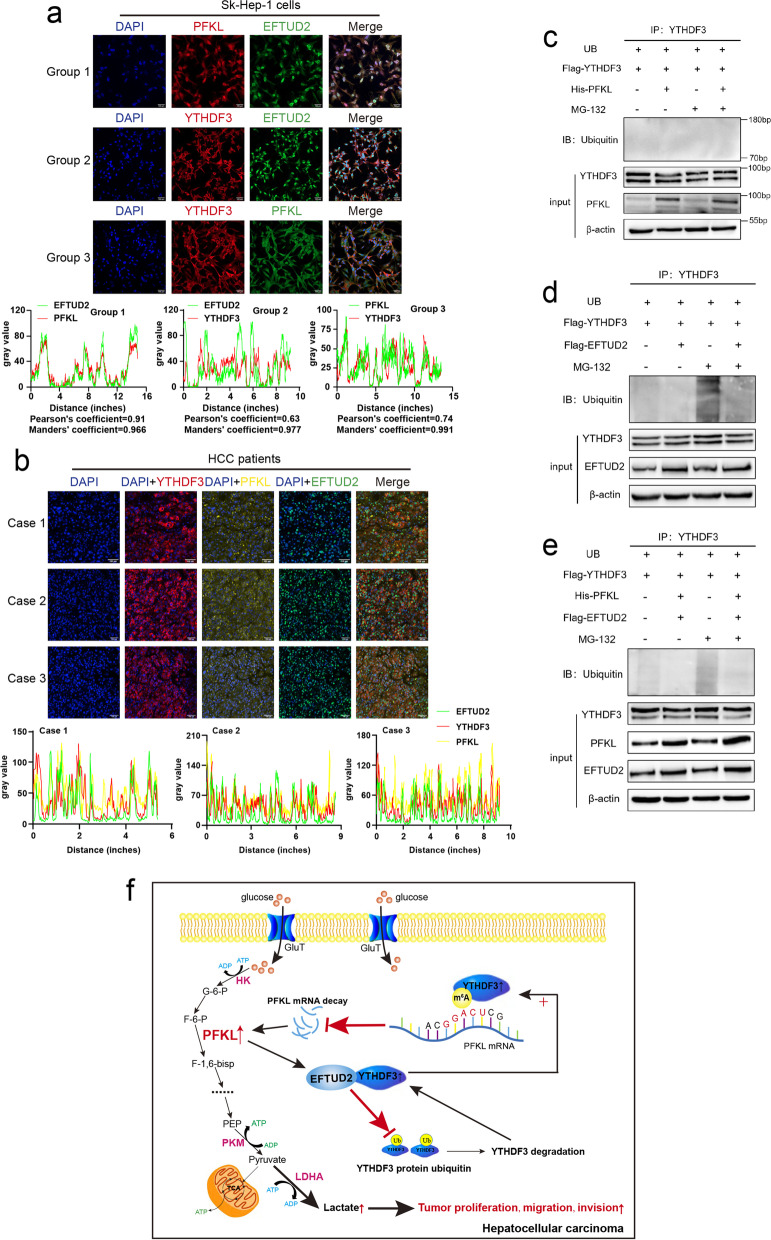
Fig. 9.
PFKL protein positively regulates YTHDF3 protein expression via inhibiting ubiquitination of YTHDF3 protein by EFTUD2. a Confocal assays of three group with Sk-Hep-1 cells incubated PFKL and EFTUd2 antibodies, YTHDF3 and EFTUd2 antibodies, or YTHDF3 and PFKL antibodies to investigate the localization between YTHDF3, PFKL and EFTUD2 (upper). Image J software was used to qualified the green, red and yellow fluorescence colocalization signal intensity, and calculated relative Pearson’s and Mander’s coefficients (lower). Scale bar 100 μm. b Multi-label immunofluorescence staining of different HCC patients to investigate the localization between YTHDF3, PFKL and EFTUD2 (upper). Image J software was used to qualified the green, red and yellow fluorescence colocalization signal intensity (lower). Scale bar 100 μm. c Ubiquitination assays of SNU449 cells co-transfected ubiquitin, YTHDF3 and PFKL plasmids. 20 nM MG-132 was added to RPMI1640 culture medium and cells were incubated continuously for 8 hours. d. Ubiquitination assays of SNU449 cells co-transfected ubiquitin, YTHDF3 and EFTUD2 plasmids. 20 nM MG-132 was added to RPMI1640 culture medium and cells were incubated continuously for 8 hours. e Ubiquitination assays of SNU449 cells co-transfected ubiquitin, YTHDF3, PFKL and EFTUD2 plasmids. 20 nM MG-132 was added to RPMI1640 culture medium and cells were incubated continuously for 8 hours. f Molecular mechanism of the relationship between YTHDF3, PFKL and EFTUD2 in HCC progression