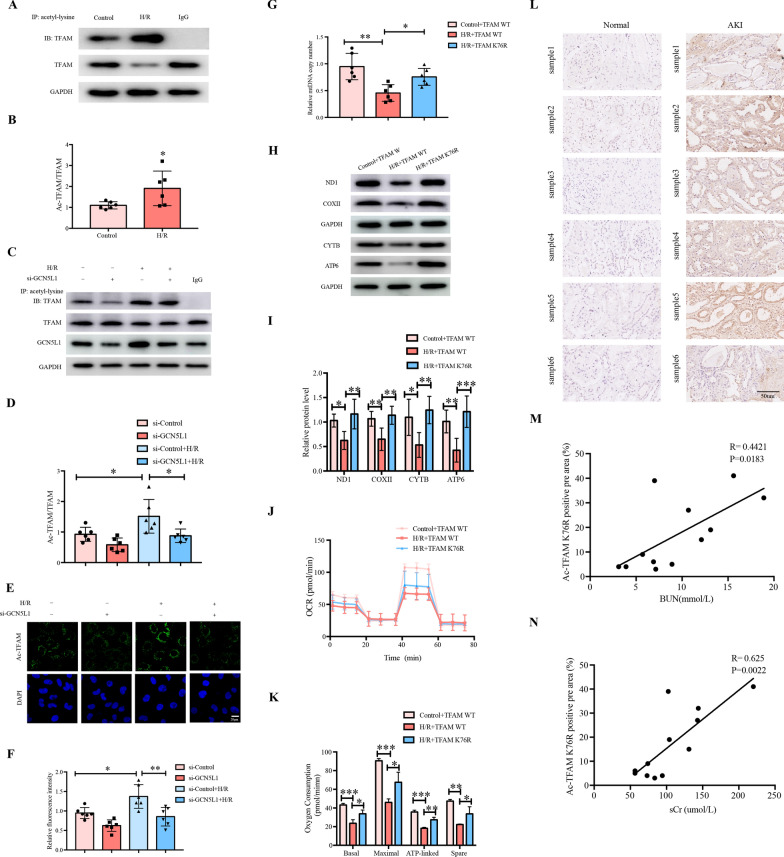
Fig. 6.
GCN5L1-mediated TFAM K76 acetylation participates in H/R-induced mitochondrial biogenesis impairment. A, B Acetylation level of TFAM was detected by immunoprecipitation in hypoxia-reoxygenation induced TECs. C, D Acetylation level of TFAM was detected by immunoprecipitation in GCN5L1 knockdown TECs under H/R treatment. E, F Acetylation level of TFAM was detected by Duolink proximity ligation assay in GCN5L1 knockdown TECs under H/R treatment. G mtDNA copy number in TECs transfected with TFAM K76 mutation plasmids under H/R treatment. H, I Protein levels of ND1, COXII, CYTB and ATP6 were detected by western blot in TECs transfected with TFAM K76 mutation plasmids under H/R treatment. J, K Bioenergetic profiles were measured by seahorse XF96 in TECs transfected with TFAM K76 mutation plasmids under H/R treatment. L Immunohistochemistry staining for acetylated TFAM K76 expression in kidney sections. M Positive correlation (Spearman r = 0.4421, P = 0.0183) between acetylated TFAM K76 IHC staining levels and BUN in all subjects. N Positive correlation (Spearman r = 0.625, P = 0.0022) between acetylated TFAM K76 IHC staining levels and serum creatinine in all subjects. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, and ***P < 0.001