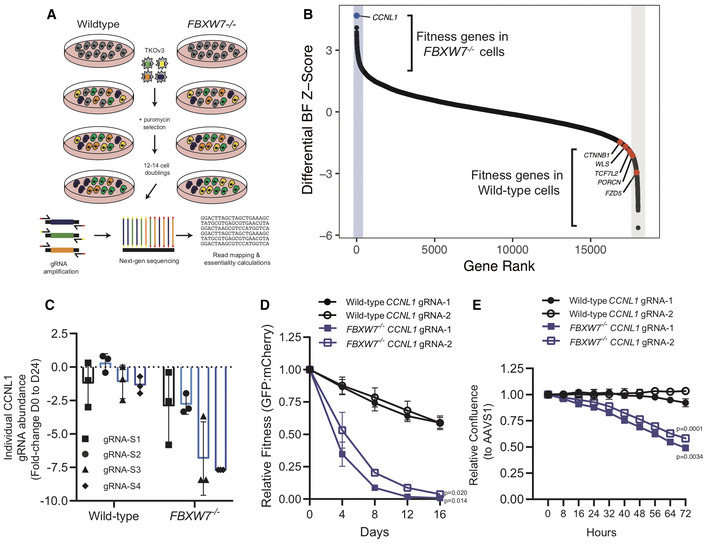
Schematic representation of genome‐wide CRISPR‐Cas9 dropout screens performed in isogenic wild‐type and FBXW7
−/− HPAF‐II cell lines.
Differential Bayes Factor Z‐score plot comparing wild‐type and FBXW7
−/− genome‐wide dropout screens.
Fold‐change abundance of individual gRNA targeting CCNL1 during the genome‐wide dropout screens from day 0 to day 24, n = 3 technical replicates per gRNA, mean ± SEM.
Multicolour competition assay in both wild‐type and FBXW7
−/− cell lines, using mCherry‐AAVS1 and GFP‐GOI, normalized to AAVS1 control cells at each time‐point (n = 3 independent replicates), mean ± SEM, one‐way ANOVA.
Proliferation assays in wild‐type and FBXW7
−/− cell lines show that knockout of CCNL1 preferentially affects FBXW7
−/− cells, normalized to AAVS1 control (n = 3 independent replicates), mean ± SEM, one‐way ANOVA.