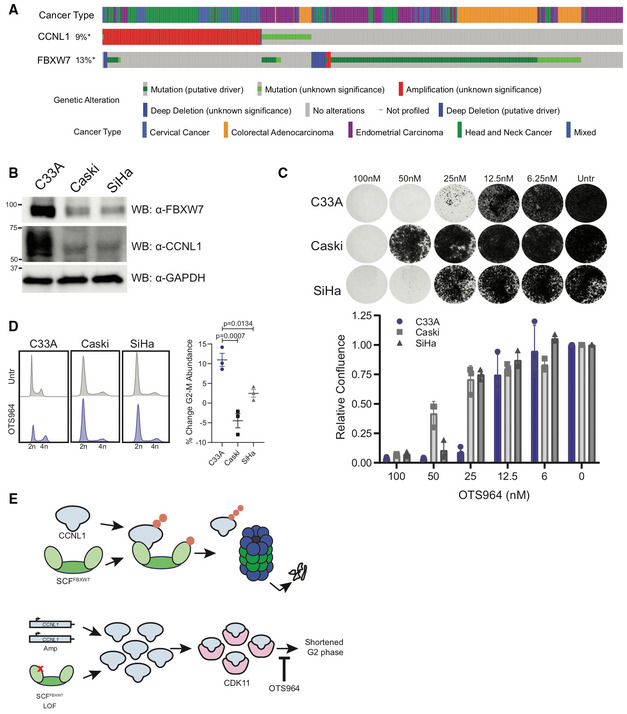
Oncoprint from cBioPortal demonstrates mutual exclusivity between FBXW7 and CCNL1 alterations.
Immunoblot of lysates from cervical cell lines demonstrating C33A cells (FBXW7
R465H) express high levels of CCNL1, representative of three independent replicates.
Clonogenic growth assay of C33A, Caski, and SiHa cells in presence of various doses of OTS964 for 14 days. Representative images of three independent replicates, quantified by crystal violet absorbance at A595 and plotted mean ± SEM.
Cell cycle distribution plots with and without 24 h OTS964 treatment, representative of three independent replicates. Normalized to untreated, mean ± SEM, one‐way ANOVA.
Model of proposed mechanism. SCF‐FBXW7 mediated ubiquitination of CCNL1 (indicated by orange circles) promotes proteasomal degradation. LOF mutations in FBXW7 or CCNL1 amplification result in an accumulation of CCNL1/CDK11 complex which shortens the G2 phase of the cell cycle and causes increased sensitivity to OTS964.