Figure 8. Long‐range interactions between promoters of housekeeping genes directly bound by ROW and developmental genes bound indirectly by ROW.
-
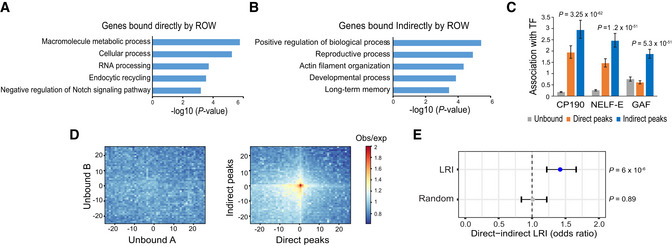
A, BThe top 5 most significantly enriched biological processes (P‐value <0.001) for (A) genes bound directly and (B) indirectly by ROW, after removing redundant terms using the REVIGO tool.
-
CThe association of three transcription factors (CP190, NELF‐E, and GAF) with genes unbound (n = 7,378), bound directly (n = 2,335), and bound indirectly by ROW (n = 3,176). Values are the odds ratios ± 95% confidence interval.
-
DPlot of aggregated Hi‐C submatrices of (left panel) random sets of promoters unbound by ROW, and (right panel) promoters bound directly and indirectly by ROW. The plots show the promoters in the center within a region of 50 kb divided into 50 bins (bin size = 1 kb). The values are the mean of observed/expected transformed submatrices (warm colors indicate higher values). The middle region on the right panel shows a high observed/expected value indicating a high level of long‐range interactions between promoters bound directly and indirectly by ROW.
-
ESignificant enrichment of long‐range interactions (LRI) between direct (n = 5,320) and indirect ROW peaks (n = 3,138) but not between randomly generated interactions. The association tests within the interactions identified in Hi‐C data were performed using the PSYCHIC tool (Ron et al, 2017). Values are the odds ratios ±95% confidence interval. Significance was calculated using the Fisher's exact test.
