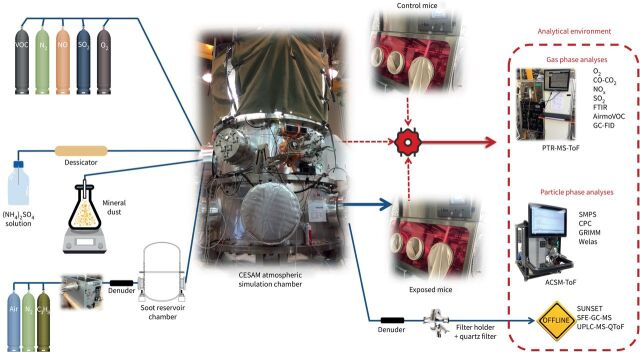
FIGURE 2.
A schematic view of the atmospheric simulation, starting to the left with a continuous introduction of air and precursors in the atmospheric simulation chamber, then under the irradiation of Xe lamps at the top of the chamber the chemistry takes place, leading after a few hours to a secondary atmosphere “feeding” the exposure device where the exposed pre-clinical models are positioned, while the reference pre-clinical samples are exposed to a reference atmosphere (air filtered from pollutants). Analytical instruments allow to qualify/quantify the pollutants present in the simulated atmosphere, both online and offline (PolluRisk platform, France). ACSM-ToF: time-of-flight aerosol chemical speciation monitor; CESAM: multiphase atmospheric experimental simulation chamber; CPC: condensation particle counter; FTIR: Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy; GC-FID: gas chromatography–flame ionisation detection; PTR-MS-ToF: proton transfer reaction time of flight mass spectrometry; SFE-GC-MS: supercritical fluid extraction with gas chromatography–mass spectrometry; SMPS: scanning mobility particle sizer; UPLC-MS-QToF: ultra-performance liquid chromatography quadrupole time of flight mass spectrometry; VOC: volatile organic compound.