Figure 5.
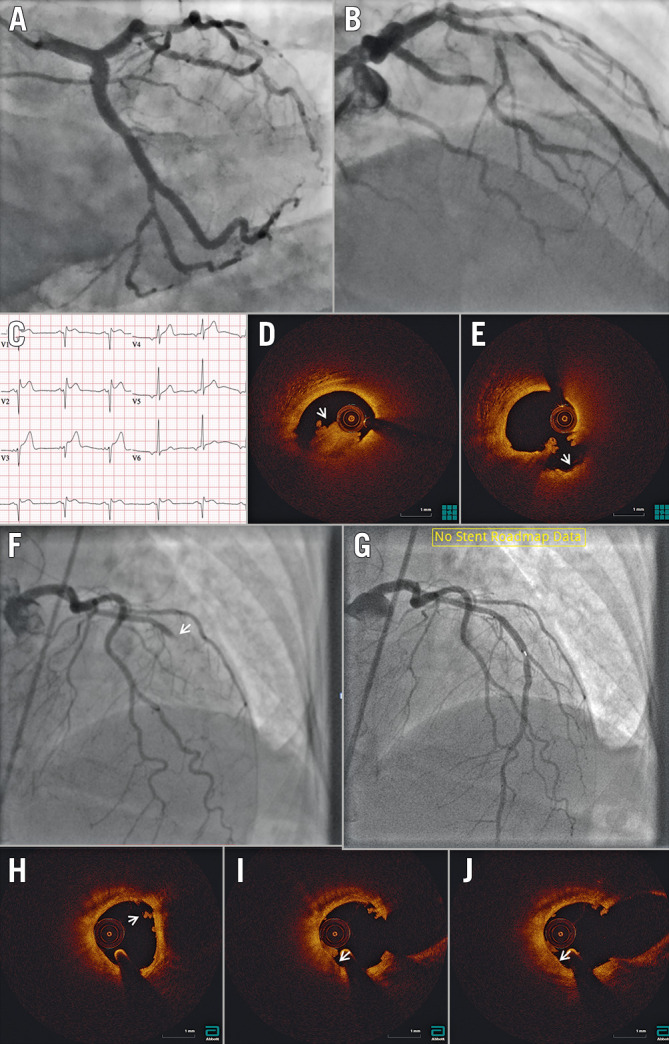
OCT in ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction. A) & B) Angiography does not identify a clear culprit lesion. C) Based on ST-segment elevation in the anterior leads, suggesting myocardial infarction with non-obstructive coronary arteries (MINOCA), optical coherence tomography (OCT) was performed in the left anterior descending coronary (LAD) artery, identifying (D) red thrombus (arrowhead) just proximal to the dominant septal. Following aspiration (E), repeat OCT shows the typical appearance of a crater with a smooth inner surface (arrowhead). F) Angiography identifies an occlusion at the mid-LAD segment (arrowhead). G) Following aspiration, repeat OCT with angiographic co-registration identifies (H) white thrombus (arrowhead) with no underlying plaque rupture. I) & J) Notably, white thrombus is adherent to a high attenuation thin-cap fibroatheroma (arrowhead), suggesting the possibility of erosion as the mechanism of MINOCA. The patient was started on dual antiplatelet therapy and the stent was not placed.
