Figure 1 -. Design and implementation of a variant-based massively parallel reporter assay.
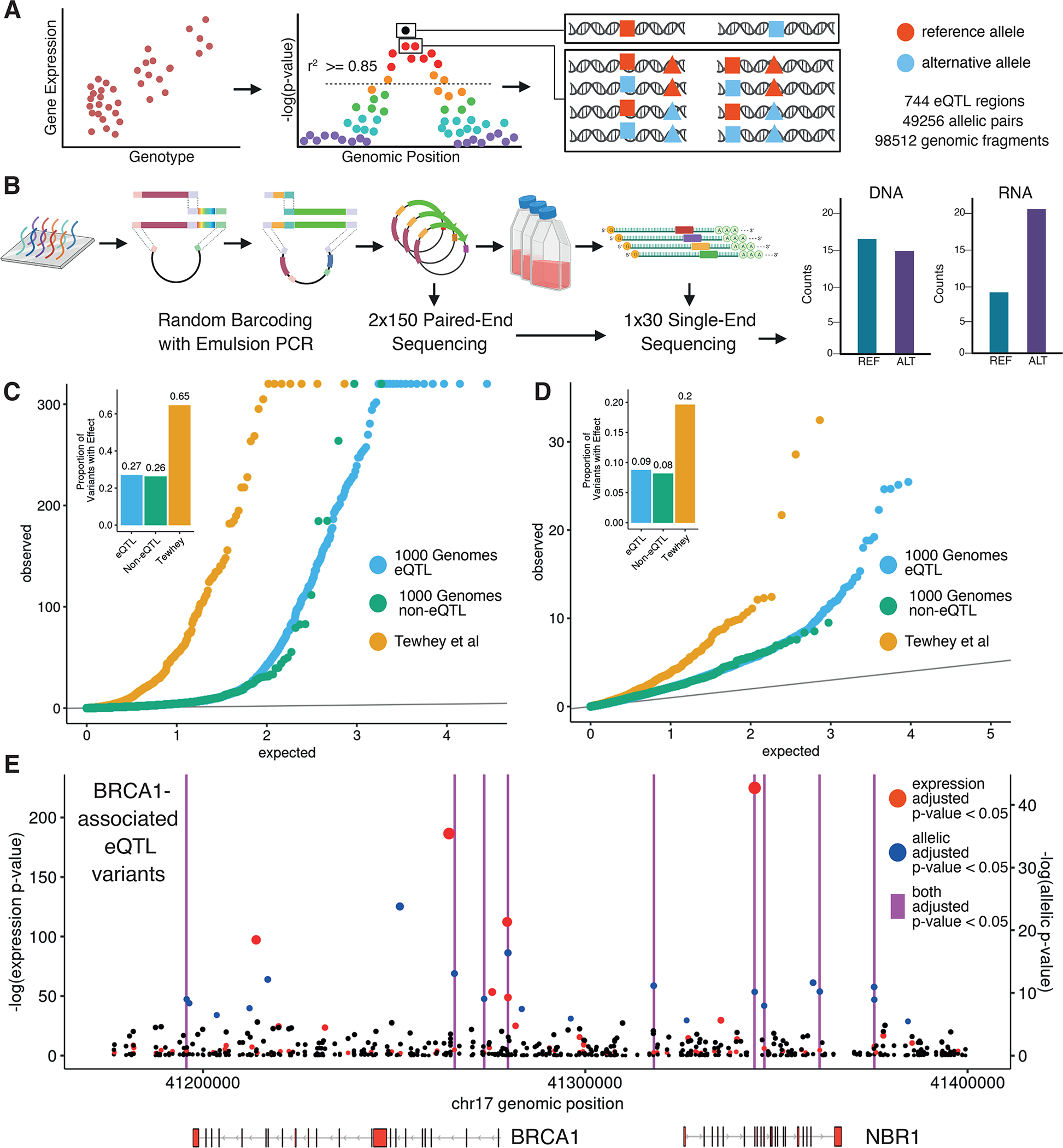
(A) Variant selection and oligonucleotide sequence design. (B) Random barcoding, sequencing and expression of the MPRA library. (C) Distribution of eQTLs (orange) and non-eQTLs (blue) from the 1000 Genomes Project compared to Tewhey et al. (green) (8) variant expression p-values (negative binomial regression) and relative effect proportions. Inset shows proportion of tested variants that are significant MPRA hits. (D) Same as in (C) but with allelic p-values (negative binomial regression) (E) Genomic position and unadjusted p-values for all tested BRCA1-associated variants with colors indicating Benjamini-Hochberg (BH) adjusted p-value <= 0.05. Vertical magenta lines indicate positions of variants that are both expression and allelic MPRA hits.
