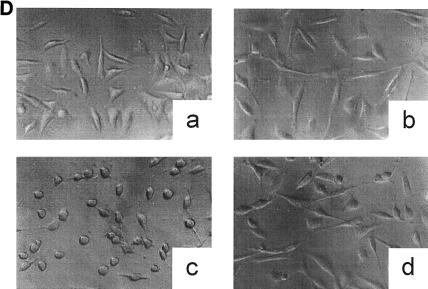
FIG. 1.
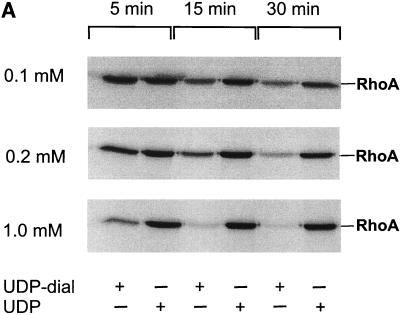
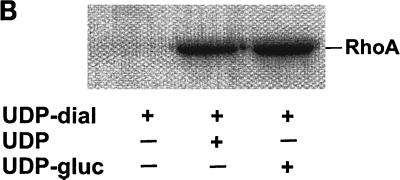
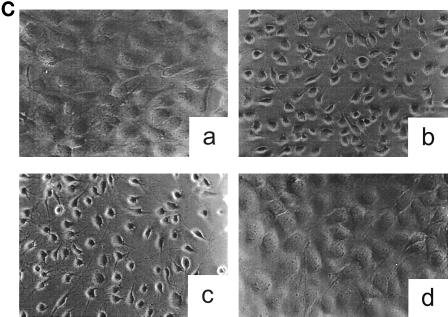
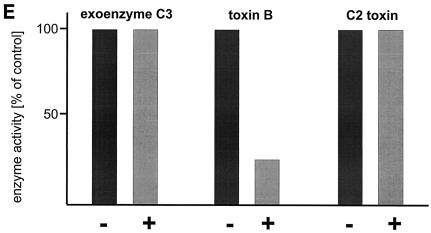
Inactivation of toxin B by treatment with UDP-dialdehyde. (A) Time course and concentration dependence of the inactivation of toxin B. Toxin B (50 μg/ml) was incubated with UDP-2′,3′-dialdehyde (UDP-dial) (concentrations as indicated) or UDP (10 mM) for the indicated times. After 1:50 dilution, toxin B-catalyzed 14C glucosylation of RhoA was tested as described in Materials and Methods. PhosphorImager data from SDS–12.5% PAGE are shown. (B) UDP and UDP-glucose (UDP-gluc) inhibit UDP-2′,3′-dialdehyde effects. Toxin B (3 μM) was treated with 1 mM UDP-2′,3′-dialdehyde in the presence of 10 mM UDP, 10 mM UDP-glucose, or buffer for 3 h. After 1:50 dilution, toxin B-catalyzed 14C glucosylation of RhoA was tested. PhosphorImager data are shown. (C) UDP inhibits UDP-2′,3′-dialdehyde effects on the cytotoxicity of toxin B. Toxin B (50 μg/ml) was treated with 1 mM UDP-2′,3′-dialdehyde (c and d) or buffer (b) in the presence of 10 mM UDP (c) or buffer (b and d) for 3 h. The remainder of the UDP-dialdehyde was removed as described in Materials and Methods. HeLa cells were incubated with 0.37 nM (0.1-μg/ml) pretreated toxin B (b to d) or PBS (a) for 90 min (phase-contrast micrographs of fixed cells are shown). a, control cells; b, untreated toxin B; c, toxin B treated with UDP-dialdehyde in the presence of UDP; d, toxin B treated with UDP-dialdehyde. (D) Competition of alkylated toxoid B with native toxin B. HeLa cells were treated with buffer (a), with 5 μg of alkylated toxoid per ml (b), with 0.05 μg of native toxin per ml (c), or with 5 μg of alkylated toxoid per ml plus 0.05 μg of native toxin per ml (d) at 37°C for 40 min. The medium was changed, and the cells were incubated for an additional 1 h. Phase-contrast micrographs of fixed cells are shown. (E) Influence of UDP-dialdehyde on other enzymatically active bacterial toxins. Exoenzyme C3 and C2I toxin from C. botulinum as well as toxin B were treated with 1 mM UDP-dialdehyde (+) or buffer (−) as described above. Thereafter, ADP-ribosyltransferase (for C21 and C3) or glucosyltransferase (for toxin B) activity was tested as described in Materials and Methods. PhosphorImager data were quantified using ImageQuant (Molecular Dynamics).