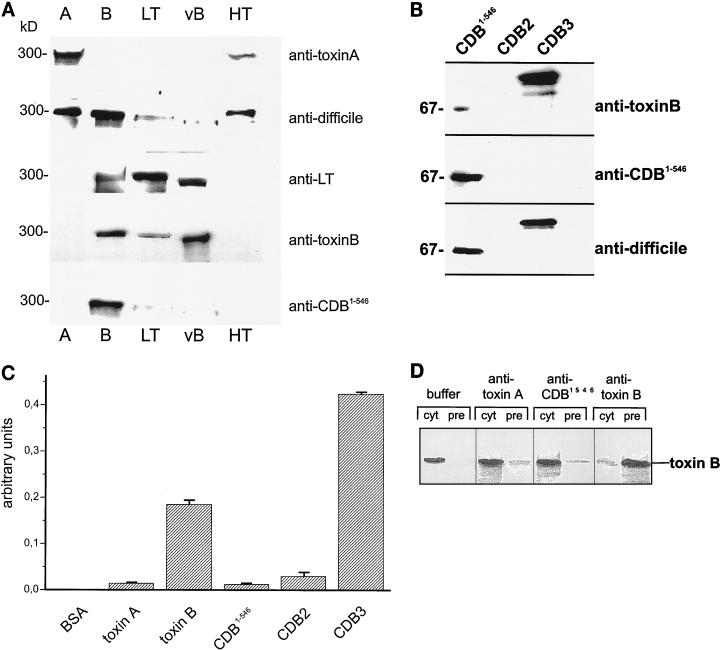
FIG. 2.
Immunoanalysis. (A) Immunoblot of large clostridial cytotoxins. Purified toxin A, toxin B, LT, the variant toxin B from strain 1470 (vB), and HT were separated by SDS–7% PAGE, electroblotted onto nitrocellulose, and probed with the antitoxin IgG as indicated on the right. ECL of the immunoblots is shown. (B) Immunoanalysis of toxin B fragments. Toxin B fragments (CDB1-546, CDB2 [amino acids 901 to 1750], and CDB3 [amino acids 1751 to 2366]) were separated by SDS-PAGE, electroblotted onto nitrocellulose, and probed with the indicated antitoxin IgG. ECL of the immunoblots is shown. (C) ELISA of holotoxins and toxin fragments with an antibody raised against holotoxin B. The indicated antigens (10 ng of each) were absorbed and incubated with antitoxin B IgG (1:3000), and bound antibody was visualized as described in Materials and Methods. BSA, bovine serum albumin. Error bars indicate standard deviations. (D) Immunoprecipitation of toxin B. Toxin B was incubated with anti-toxin A, anti-CDB1-546, anti-toxin B, or PBS for 20 min on ice, followed by the addition of protein A/G-agarose. Supernatants (cyt) and precipitated proteins (pre) were analyzed with anti-toxin B. ECL of the immunoblots is shown.