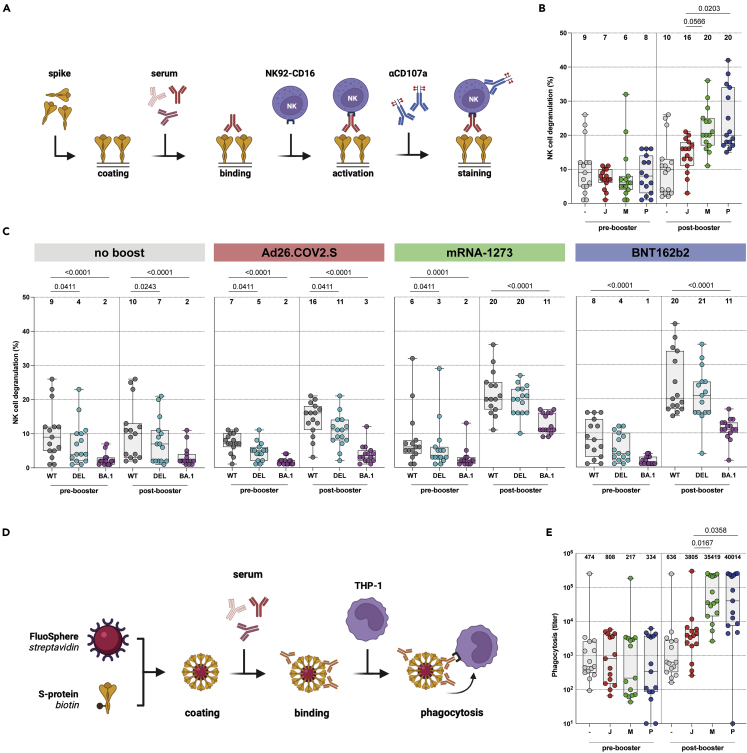
Figure 2.
Fc-mediated antibody functions are boosted by homologous or heterologous vaccination, but less functional against the Omicron BA.1 variant
(A) Antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity (ADCC) assay methodology.
(B) NK cell degranulation (%) to the ancestral SARS-CoV-2 pre- and post-booster vaccination after no boost (grey), Ad26.COV2.S boost (red), mRNA-1273 boost (green), or BNT162b2 boost (blue). Median percentages are depicted above graph.
(C) NK cell degranulation to ancestral SARS-CoV-2 (grey), Delta (cyan), or Omicron BA.1 (pink) variants pre- and post-booster vaccination. Median percentages are depicted above graph.
(D) Antibody-dependent cell-mediated phagocytosis (ADCP) assay methodology.
(E) Phagocytosis-mediating antibodies to ancestral SARS-CoV-2 pre- and post-booster vaccination. Geometric mean titers (GMT) are depicted above graph. - = no boost, J = Ad26.COV2.S, M = mRNA-1273, P = BNT162b2, WT = ancestral virus, delta = Delta variant, BA.1 = Omicron BA.1 variant. Symbols represent individual donors (n = 15 per group). Box plot depicts the median with range (min to max). Kruskal-Wallis test followed by Dunn’s multiple comparisons was performed for comparison of vaccine responses between groups; only differences between Ad26.COV2.S and mRNA-1273, or Ad26.COV2.S and BNT162b2 are shown in the figure (if a significant difference was detected). Friedman test followed by Dunn’s multiple comparisons was used to compare vaccine responses to variants within each group; only differences between ancestral SARS-CoV-2 and variants are shown in the figure (if a significant difference was detected).