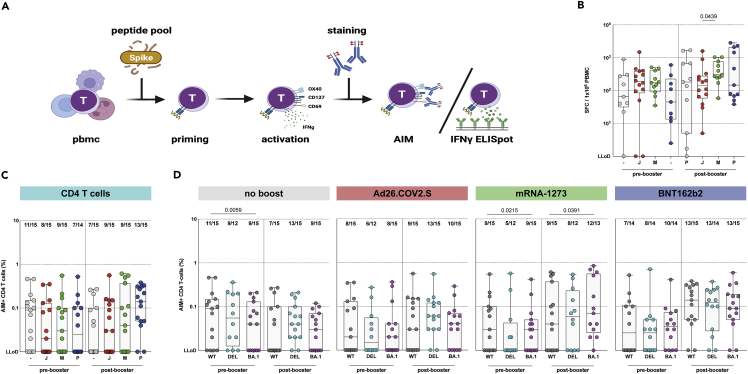
Figure 5.
SARS-CoV-2-specific CD4 T cells cross-react with Omicron BA.1
(A) Activation-induced marker (AIM) assay and IFN-ɣ ELISPOT methodology.
(B) IFN-ɣ secreting T cells after stimulation with an overlapping S peptide pool from the ancestral SARS-CoV-2 pre- and post-booster vaccination, after no boost (grey, n = 9), Ad26.COV2.S boost (red, n = 14), mRNA-1273 boost (green, n = 11), or BNT162b2 boost (blue, n = 11).
(C) Comparison of CD4 T-cell responses to ancestral SARS-CoV-2.
(D) CD4 T-cell responses against ancestral SARS-CoV-2 (grey), Delta (cyan), or Omicron BA.1 (pink) variants pre- and post-booster vaccination. Fraction of donors with measurable AIM-positive T-cells is indicated above the box-plots. - = no boost, J = Ad26.COV2.S, M = mRNA-1273, P = BNT162b2, WT = ancestral virus, delta = Delta variant, BA.1 = Omicron BA.1 variant. Symbols represent individual donors. Box plot depicts the median with range (min to max). Kruskal-Wallis test followed by Dunn’s multiple comparisons was performed for IFN-ɣ ELISPOT. Mann-Whitney U test was performed for comparison of vaccine groups Ad26.COV2.S and mRNA-1273, and Ad26.COV2.S and BNT162b2 (shown in panel C); a p-value of 0.025 was considered significant after Bonferroni correction. Wilcoxon rank test was performed for the comparison of variant-specific T-cell responses between ancestral SARS-CoV-2 and variants (shown in panel D); a p-value of 0.025 was considered significant after Bonferroni correction.