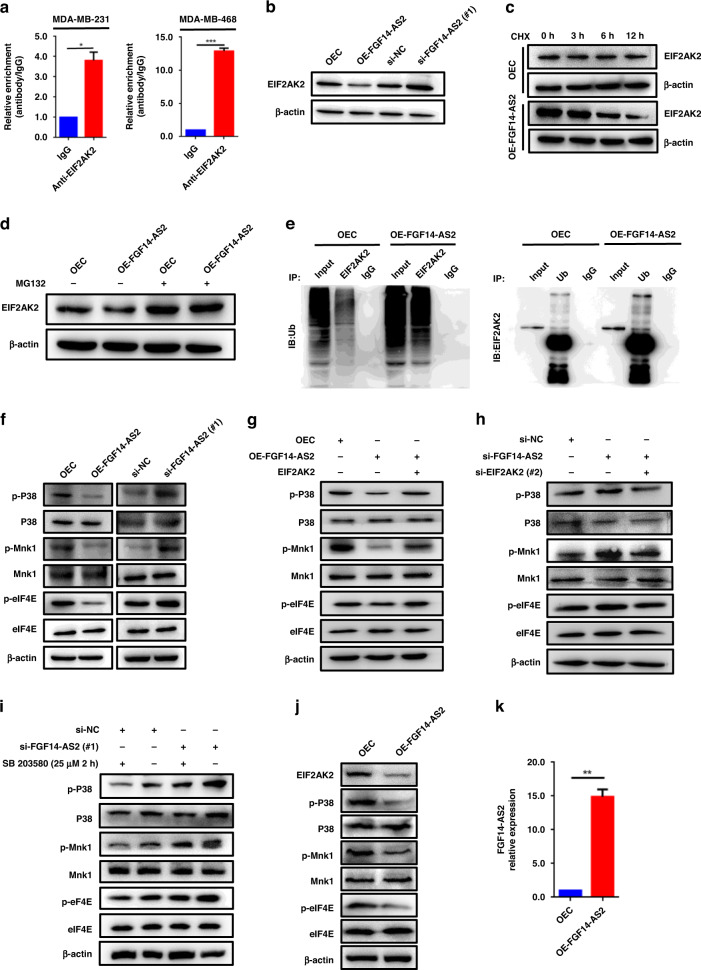
Fig. 5. FGF14-AS2 inhibits eIF4E phosphorylation via the EIF2AK2/p38 signalling pathway.
a RIP assay was performed using indicated cell lysates and anti-EIF2AK2 antibodies, and the coprecipitated RNAs were subjected to qRT-PCR to detect FGF14-AS2. The fold enrichment of FGF14-AS2 in the EIF2AK2 pellet is shown relative to its matching IgG control. b EIF2AK2 levels in FGF14-AS2-overexpressing and FGF14-AS2-knockdown MDA-MB-231 cells were detected using western blotting. c, d EIF2AK2 levels in FGF14-AS2-overexpressing and control cells treated with Cycloheximide (CHX) (50 μg/ml) (c) or MG132 (25 µM, 4 h) (d) were detected using western blotting. e Co-IP assays were performed with either anti-EIF2AK2 or anti-ubiquitin (Ub) antibodies in FGF14-AS2-overexpressing and control cells. f p-p38, p38, p-Mnk1, Mnk1, p-eIF4E and eIF4E levels were examined using western blotting in MDA-MB-231 cells with FGF14-AS2 overexpression or knockdown. g, h p-p38, p38, p-Mnk1, Mnk1, p-eIF4E and eIF4E levels were examined using western blotting in MDA-MB-231 cells with both FGF14-AS2 and EIF2AK2 overexpression (g) and with both FGF14-AS2 and EIF2AK2 knockdown (h). i p-p38, p38, p-Mnk1, Mnk1, p-eIF4E and eIF4E levels were examined using western blotting in MDA-MB-231 cells with FGF14-AS2 knockdown and SB 203580 treatment (25 µM) for 2 h. j EIF2AK2, p-p38, p38, p-Mnk1, Mnk1, p-eIF4E and eIF4E AS2 levels in the tibiae of mice injected with FGF14-AS2 OE and control cells were detected by western blotting. k FGF14-AS2 levels in the tibiae of mice injected with FGF14-AS2 OE and control cells were detected by qRT-PCR. The data are shown as the mean ± s.d. of at least three independent experiments. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.005, ***P < 0.001.