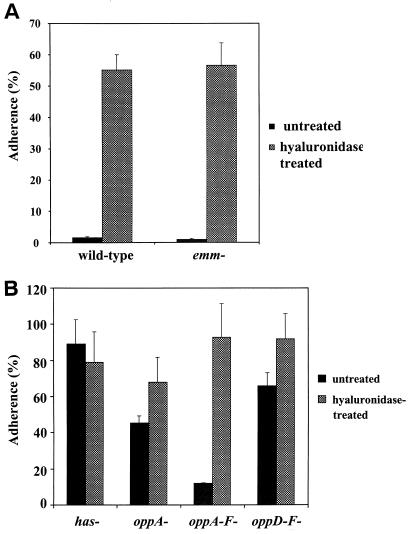
FIG. 1.
Adherence of wild-type and emm mutant strains (A) and has and opp mutant strains (B) of M49-protein S. pyogenes to cultured human keratinocytes at 37°C with (hatched bars) or without (shaded bars) enzymatic digestion of the bacterial hyaluronic acid capsule achieved by incubation with 10 μg of hyaluronidase per ml for 30 min prior to and during the adherence assay. Keratinocytes were isolated from neonatal human foreskins and grown to confluence in six-well tissue culture plates. To initiate adherence, keratinocyte cultures were inoculated with 108 CFU of l-[3H]leucine-radiolabeled S. pyogenes per ml. To calculate the percent adherence, the total CFU remaining in triplicate six-well keratinocyte cultures after washing and vortexing away the nonadherent bacteria minus the adherent CFU in wells lacking keratinocytes was divided by the total CFU in the supernatant plus those on the monolayer (in the absence of washing and vortexing) at the end of 3 h of incubation. Error bars represent the standard deviation.