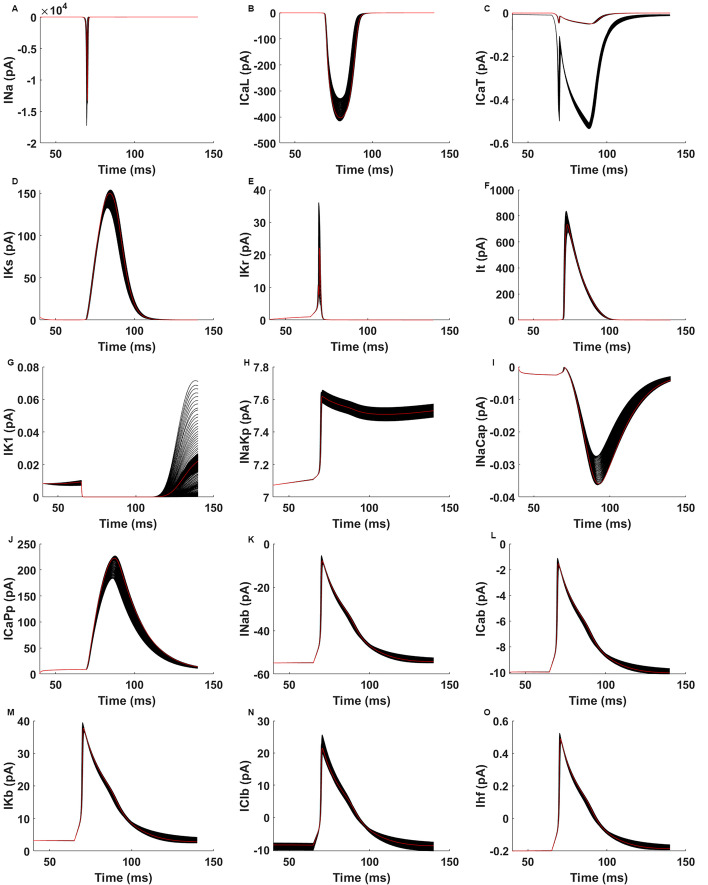
Fig. 3.
A through O illustrate the outcomes of the simulation following the application of the perturbations to channel conductances. The control currents are shown by the red lines in the illustration. Here, A INa is Na+ current, B ICaL is L-Type (long-opening) Ca2+ current, C ICaT is T-Type (transient) Ca2+ current, D IKs is slowly activated outward rectifier K+ current, E IKr is rapidly activated outward rectifier K+ current, F It is transient outward K+ current, G IK1 is inward rectifier K+ current, H INaKp is Na+-K+ pump current, I INaCap is Na+-K+ exchanger (NCX) current, J ICap is sarcolemmal Ca2+ pump current, K INab is Na+, L ICab is Ca2+, M IKb is K+, N IClb is Cl− background currents, and O Ihf is hyperpolarization-activated current