Figure 3.
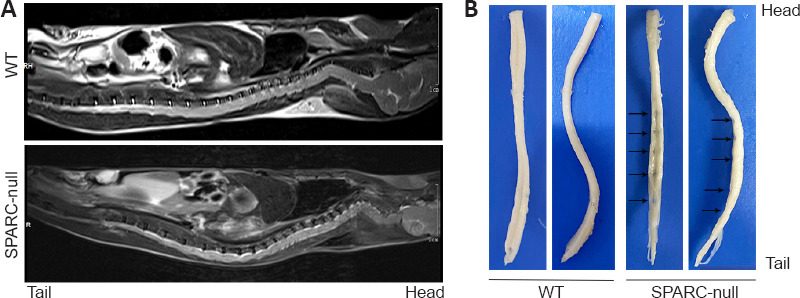
The absence of SPARC induces disc herniation in mice.
(A) MRI of the entire spine of mice. (B) The whole segment of the spinal cord after sampling and fixation. Compression was seen at different spinal cord levels, especially in the lumbar segments, in SPARC-null mice compared with the WT control. The arrows show traces of spinal cord compression. MRI: Magnetic resonance imaging; SPARC: secreted protein, acidic and rich in cysteine.
