Figure 1.
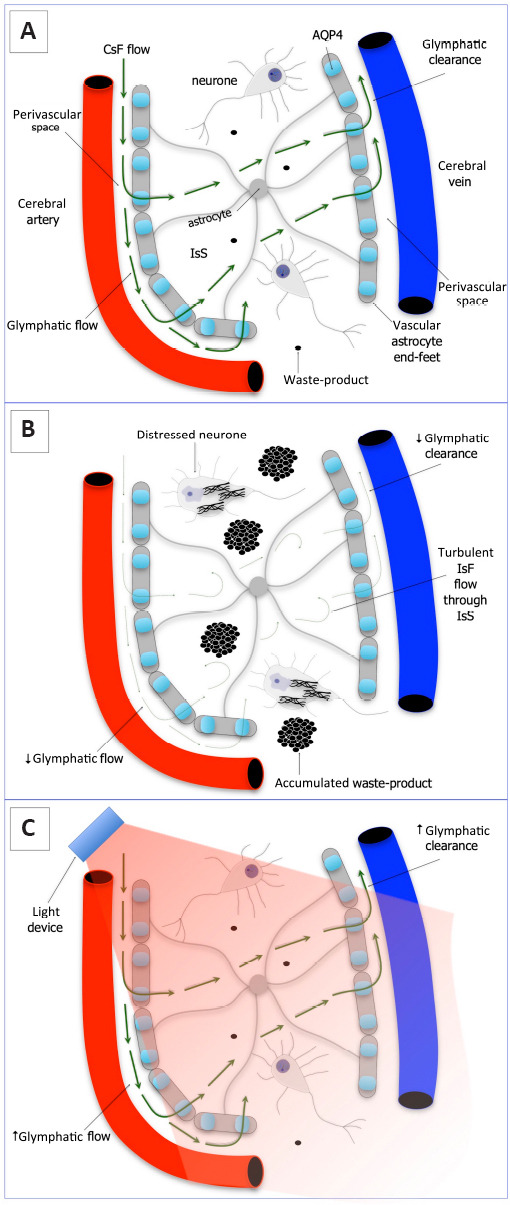
Schematic diagram of the glymphatic system of the brain.
(A) Normal: cerebrospinal fluid (CsF) flows into interstitial space (IsS) through the perivascular space and aquaporin 4 (AQP4) molecule on astrocytes. The interstitial fluid (IsF) is then cleared away into the venous system, together with any cellular waste-products (e.g., β-amyloid). This is the so-called glymphatic system. (B) Disease (or poor quality sleep): glymphatic flow and clearance are much reduced and the flow of IsF through IsS becomes turbulent. This leads to the accumulation of waste products in the IsS (e.g., that may lead to β-amyloid plaque formation), leading to distress and dysfunction in the surrounding neurons (eg, that may lead to the development of neurofibrillary tangles). (C) Photobiomodulation-treated: glymphatic flow and clearance are improved/restored and the surrounding neuropathology is reduced. We suggest that photobiomodulation may work to increase the permeability of the aquaporin-4 water channels on the astrocytes, thereby helping to increase the flow of fluid through the brain. Adapted from Louveau et al. (2017) and Brodziak et al. (2018).
