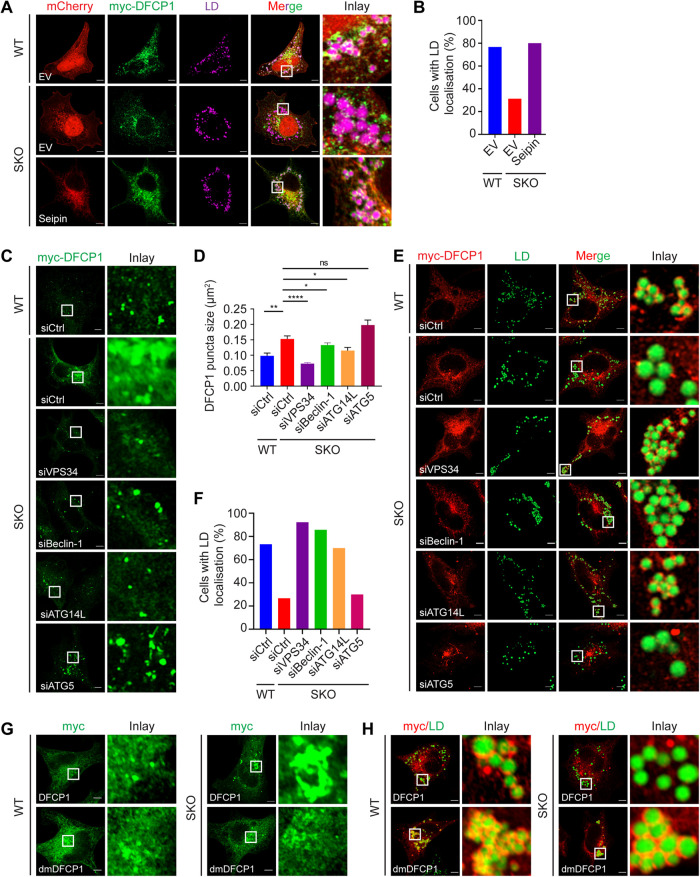
FIGURE 2:
The association of DFCP1 with LDs is regulated by seipin and PI(3)P. (A) Loss of LD association by myc-DFCP1 in SKO cells. WT and SKO HeLa cells expressing myc-DFCP1 and mCherry-EV or mCherry-seipin were treated with 400 µM oleate for 6 h, fixed, and stained with anti-myc antisera. LDs were then stained with HCS LipidTOX Deep Red Neutral Lipid Stain (purple). (B) Percentage of cells with LD association (continuous encircling structures around LDs) by myc-DFCP1 as shown in D, n = 30 cells, data from a representative experiment. (C) Knocking down ATG14L, Beclin-1, or VPS34 but not ATG5 reduced the size and number of DFCP1 puncta in SKO cells. WT and SKO HeLa cells were transfected with the indicated siRNAs, fixed, and stained with anti-myc antisera. (D) Quantification of the area of DFCP1 puncta as shown in C. Mean ± SEM, n > 154 puncta over three biological experiments, *, p < 0.05; **, p < 0.01; ****, p < 0.0001, calculated by one-way ANOVA with Dunnett’s multiple comparisons test. (E) Knocking down ATG14L, Beclin-1, or VPS34 but not ATG5 restored LD association by DFCP1 in SKO cells. WT and SKO cells were transfected with the indicated siRNAs. The cells were then treated with oleate for 6 h, fixed, and stained with anti-myc antisera. LDs were stained with BODIPY493/503 (green). (F) Percentage of cells with LD association by DFCP1 as shown in E. n = 30 cells, data from a representative experiment. (G) Distribution of myc-DFCP1 and myc-dmDFCP1 in WT and SKO HeLa cells. (H) Distribution of myc-DFCP1 and myc-dmDFCP1 (both in red) in WT and SKO HeLa cells treated with 400 µM oleate for 16 h. LDs were stained with BODIPY493/503 (green). Scale bars represent 5 μm.