Figure 1.
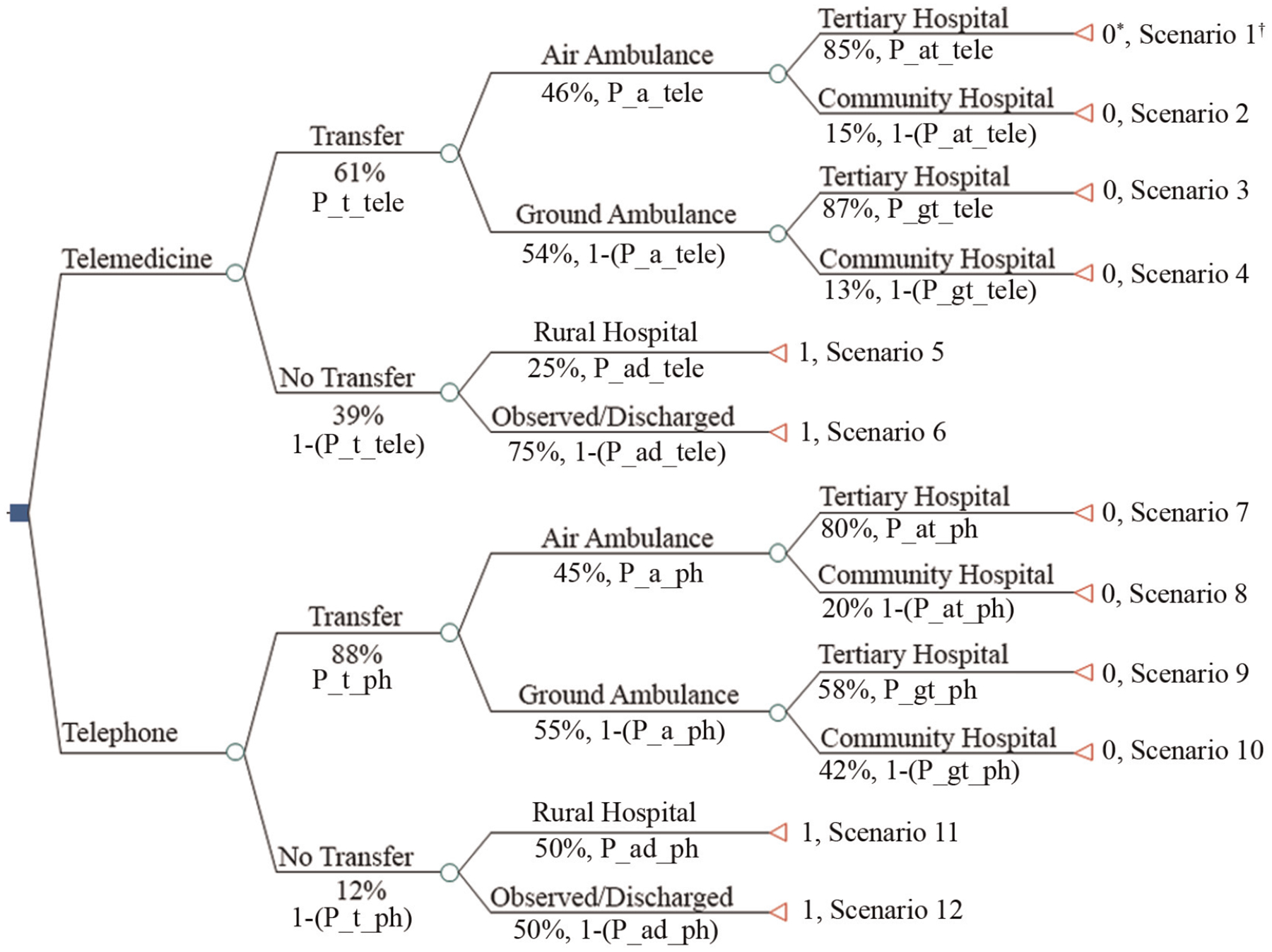
Decision tree with observed patient transfer rates and cost components in the base-case analysis. *The effectiveness measure was avoided patient transfers after children received telemedicine or telephone consultations. 0 = patient transfers, 1 = avoided patient transfers. †The total cost estimate for scenario 1: telemedicine operational cost + rural emergency department (ED) visit cost + air ambulance transfer cost + tertiary hospital treatment cost. The total cost estimate for scenario 2: telemedicine operational cost + rural ED visit cost + air ambulance transfer cost + community hospital treatment cost. The total cost estimate for scenario 3: telemedicine operational cost + rural ED visit cost + ground ambulance transfer cost + tertiary hospital treatment cost. The total cost estimate for scenario 4: telemedicine operational cost + rural ED visit cost + ground ambulance transfer cost + community hospital treatment cost. The total cost estimate for scenario 5: telemedicine operational cost + rural ED visit cost + rural hospital treatment cost. The total cost estimate for scenario 6: telemedicine operational cost + rural ED visit cost. The total cost estimate for scenario 7: rural ED visit cost + air ambulance transfer cost + tertiary hospital treatment cost. The total cost estimate for scenario 8: rural ED visit cost + air ambulance transfer cost + community hospital treatment cost. The total cost estimate for scenario 9: rural ED visit cost + ground ambulance transfer cost + tertiary hospital treatment cost. The total cost estimate for scenario 10: rural ED visit cost + ground ambulance transfer cost + community hospital treatment cost. The total cost estimate for scenario 11: rural ED visit cost + rural hospital treatment cost. The total cost estimate for scenario 12: rural ED visit cost.
