Fig. 2.
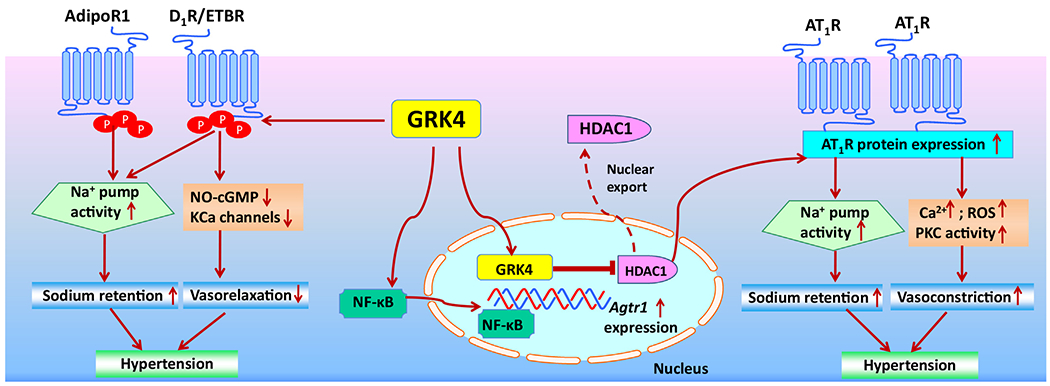
GRK4-mediated regulation of blood pressure via the kidneys and arteries.
GRK4 regulates blood pressure by modulating GPCRs and non-GPCRs in the kidneys and arteries by several mechanisms: 1) renal or arterial GRK4 increases the phosphorylation of D1R, AdipoR1, and ETBR impairs receptor-mediated inhibition of the sodium pump (Na+/K+-ATPase) and attenuates receptor-induced vasorelaxation, subsequently leading to hypertension; 2) renal GRK4 promotes HDAC1 egress from the nucleus into the cytoplasm, which up-regulates Agtr1 expression and the ability of AT1R to increase the activity of the sodium pump (Na+/K+-ATPase), which results in an increase in renal sodium reabsorption and extracellular fluid volume, and consequently hypertension; 3) in the arteries, GRK4 increases NF-κB activity with more NF-κB binding to the AT1R promoter, which increases Agtr1 expression and AT1R protein abundance, intracellular calcium concentration, ROS production, and PKC activity, enhancing vasoconstriction and consequently hypertension.
Abbreviations: AT1R, angiotensin II receptor type 1; AdipoR1, adiponectin receptor 1; cGMP, cyclic guanosine monophosphate; D1R, dopamine D1 receptor; ETBR, endothelin receptor type B; GRK4, G protein-coupled receptor kinase 4; HDAC1, histone deacetylase type 1; KCa: calcium-activated K+ channel; NF-κB, nuclear factor kappa B; NO: nitric oxide; PKC: protein kinase C; ROS, reactive oxygen species.
