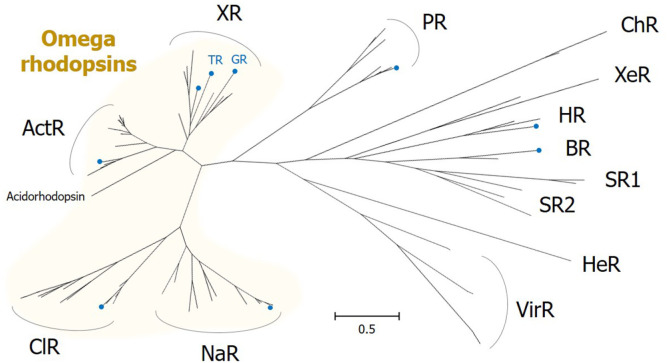
Fig. 4. Phylogenetic relationships between omega rhodopsins and other microbial rhodopsin families.
The maximum-likelihood method using the Jones-Taylor-Thornton matrix-based model of amino acid substitution rates with empirical amino acid frequencies and the gamma model was used. Representative microbial rhodopsins were aligned by MUSCLE. Evolutionary analyses were conducted in MEGA X. Blue-colored circles on the tip of some branches indicate the rhodopsins listed in Fig. 2. NDQ motif-containing sodium-pump rhodopsin, NaR; NTQ motif-containing chloride-pump rhodopsin, ClR; xanthorhodopsin, XR; Gleobacter rhodopsin, GR; thermophilic rhodopsin, TR; actinorhodopsin, ActR; proteorhodopsin, PR; bacteriorhodopsin, BR; halorhodopsin, HR; channel rhodopsin, ChR; sensory rhodopsin, SR; xenorhodopsin, XeR; heliorhodopsin, HeR; viral rhodopsin, ViR.