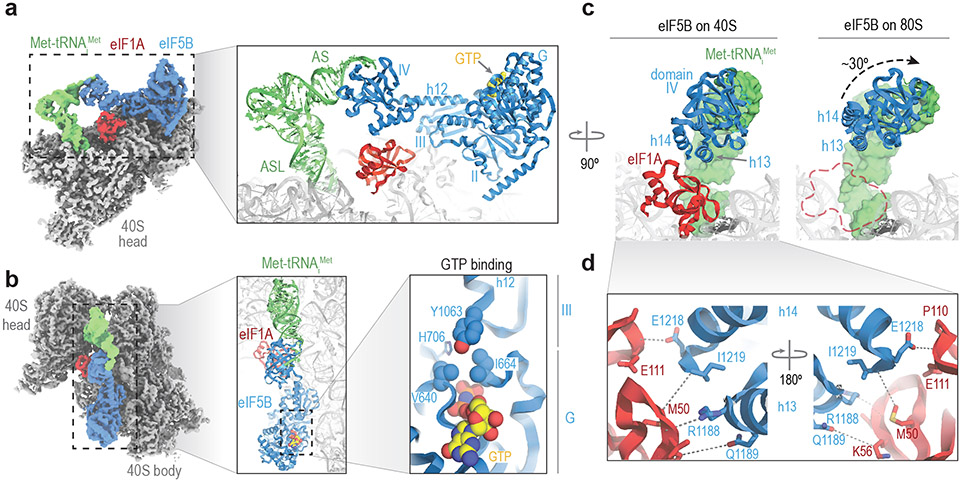
Figure 3. Cryo-EM structure of an eIF1A and eIF5B-bound 48S initiation complex.
a. Post-processed density for the cryo-EM map (overall resolution 3.2 Å) of the eIF1A and eIF5B-bound initiation complex, with 40S subunits colored grey, Met-tRNAiMet green, eIF1A red, and eIF5B blue. Right, view of the refined molecular model derived from the cryo-EM data centered around eIF1A, with GTP colored yellow. Domains of eIF5B and regions of Met-tRNAiMet are indicated. ASL, anti-codon stem loop; AS, acceptor stem. The cryo-EM data and final atomic coordinates were deposited at the EMDB and PDB with identifier codes 26067 and 7TQL, respectively. b. Left, zenithal view of the cryo-EM map with components colored as in panel A. Middle, view of the molecular model along the acceptor stem axis of Met-tRNAiMet. Right, detailed view of the GTP-binding pocket of eIF5B. Tyrosine residue 1063, which belongs to eIF5B domain III, collaborates with G-domain residues V640 and I664, part of the "hydrophobic gate", to protect the γ-phosphate of GTP from hydrolysis. c. Corresponding views of eIF5B domain IV in the 40S state with eIF1A present (left) and after 60S joining and eIF1A departure (right). Departure of eIF1A allows for an approximately 30° rotation of eIF5B domain IV towards the 60S subunit, bringing the acceptor stem of Met-tRNAiMet closer to the peptidyl transfer center (PTC). d. Zoomed view of the eIF5B-eIF1A interface. Terminal eIF5B α-helices h13 and h14 approach eIF1A, stabilizing weak interactions (>4Å interacting distance) nucleated around eIF1A methionine residue 50 and eIF5B residue isoleucine 1219.