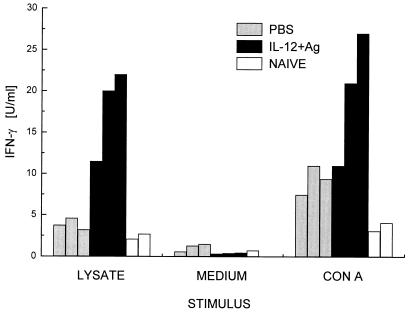
FIG. 5.
Comparison of IFN-γ secretion by CD4+ T cells of protected and nonprotected C57BL/6 mice. CD4+ T cells were prepared from lymph nodes draining the site of infection of cured mice vaccinated with IL-12 and rMBAP, rCP, and rGP63 (see Fig. 2) or of PBS mock-treated mice with progressive disease. For control purposes, CD4+ T cells were also enriched from corresponding lymph nodes of naive, noninfected animals. The enriched cell populations were stimulated with a freeze-thawed lysate of L. mexicana promastigotes presented by syngeneic splenocytes in vitro. Antigen-specific IFN-γ production was determined in the supernatants and compared to the production of this cytokine in cultures treated with concanavalin A or medium alone. Values represent the mean of duplicate cultures of CD4+ cells from individual mice (three animals of each infected group and two naive controls). The lymphokine content varied by less than 10% between duplicates. Antigen-specific IFN-γ production by CD4+ cells from vaccinated mice was significantly higher than that by cells from mock-treated mice (P ≤ 0.05; in a Wilcox ranking test).