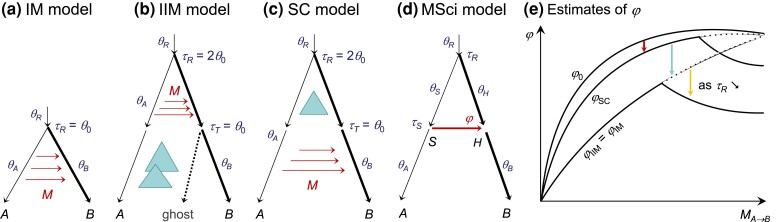
Fig. 1.
(a–c) Three MSC-M models for two species A and B used to generate data: IM (isolation with migration), IIM (isolation with initial migration), and SC (secondary contact). The IIM model is an instance of the MSC-M model with a ghost species at node T and with migration from species A to T (b). Similarly, the SC model (c) is a case of the MSC-M model with . Note that is the time when migration stopped in the IIM model and the time when migration started in the SC model. In the numerical calculations and in the simulations, we assumed the population size for the thin branches and for the thick branches, and the migration rate was migrants from A to B per generation. Note that in our setup, the time period of gene flow is in all three models. (d) The introgression (MSci) model used to analyze the data. (e) A schematic summary of the estimate of the introgression probability () in the MSci model (d) when the data are generated under the MSC-M models of a–c. The sudden drop in as increases coincides with an underestimation of and overestimation of .