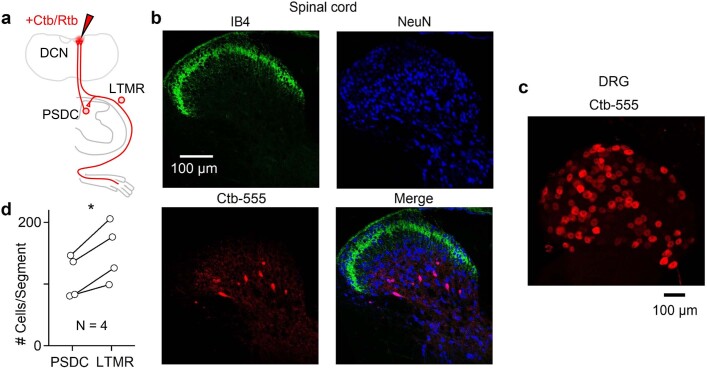
Extended Data Fig. 3. Prevalence and anatomical location of PSDCs.
Choleratoxin-B (Ctb) or Retrobeads (Rtb) were injected into the DCN or C1 DC to label PSDCs and Aβ-LTMRs that project to the DCN. Two different tracers were used in order to avoid potential differences in LTMR vs. PSDC uptake efficiency. Small injections were performed in order to avoid off-target labeling in the spinal cord, and to compare the relative number of thoracic LTMRs and PSDCs. The number of LTMRs and PSDCs per thoracic spinal segment within the same animal was compared. PSDCs were found in lamina III-IV as described by others6,31,56. Experiment was performed in 4 animals. (N = 4 animals). a, Schematic showing injection of retrograde tracer into the brainstem and uptake by either PSDCs in the dorsal horn of the spinal cord or Aβ-LTMRs in the DRG. b, 10 µm Z-projection of a transverse thoracic spinal cord section (60 µm thick) with immunofluorescence of IB4 (top left, green), NeuN (top right, blue), Ctb-555 (bottom left), and merged images (bottom right). Experiment was repeated in 4 animals (see d for summary). c, Single plane image of a whole-mount thoracic DRG containing sensory neurons labeled with Ctb-555 from the same animal shown in b. Experiment was repeated in 4 animals (see d for summary). d, Comparison of number of Ctb or Rtb labeled cells in the thoracic spinal cord. Each marker pair is the average from one animal, showing the average number of cells labeled in 1-2 DRGs, and the number of PSDCs estimated to exist in one spinal segment (1000 µm length of spinal cord) based on the average number of PSDCs labeled in 10–20 spinal sections (60 µm thickness). p = 0.017, paired t-test.