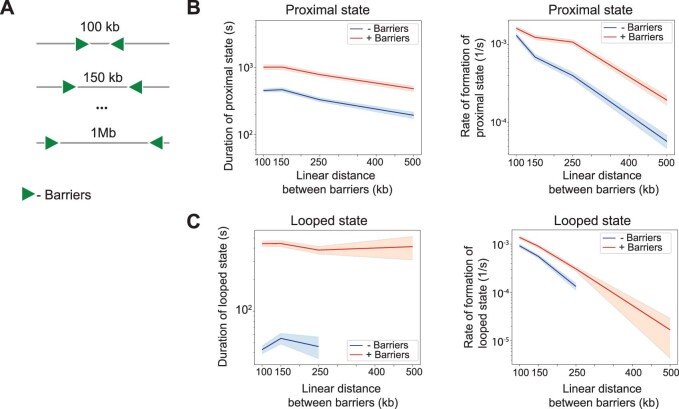
Extended Data Fig. 10. Polymer simulations of landscapes with two barriers at different distances.
A. Scheme of simulated polymers with varying distances between (optional) convergent loop extrusion barriers, corresponding to 100, 150, 250, 500, and 1000 kb. B. Duration (left) and rate of formation (right) of the HMM proximal state detected on simulated pairwise distances (after addition of experimental error) between monomers in the presence or absence of extrusion barriers, as a function of the intervening linear genomic distance. Lines are means, shaded areas are s.e.m. Note that the average duration of the HMM proximal state slightly decreases although the average duration of the underlying cohesin-mediated CTCF-CTCF interaction doesn’t (see panel C). This is due to non-CTCF mediated interactions, which also contribute to the proximal state, and decrease with increasing genomic distance. C. Average duration (left) and rate of formation (right) of the looped state (that is cohesin-mediated CTCF-CTCF interaction) extracted from polymer simulations. Lines are means, shaded areas are s.e.m.