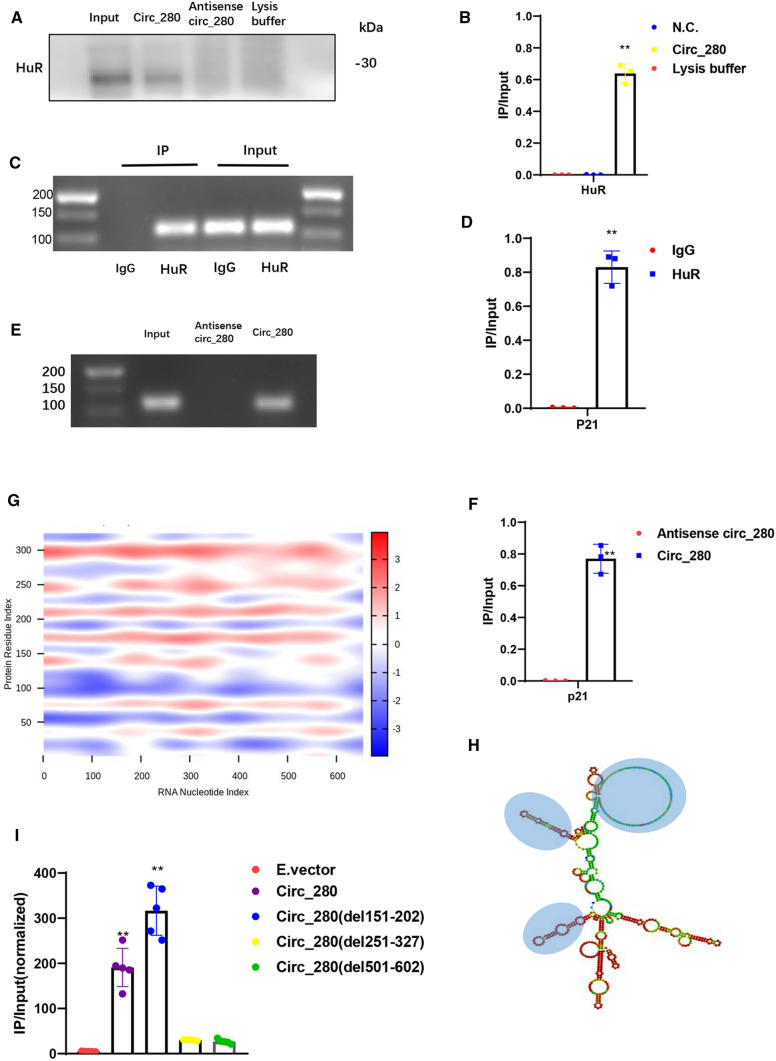
Fig. 3.
Hsa_circ_0000280 binds ELAVL1. A, B RNA pull-down assay of hsa_circ_0000280 in vitro. Negative controls comprised antisense RNA of hsa_circ_0000280 and blank lysis buffer. Western blots of ELAVL1 protein (n = 3, p < 0.0001; Student t tests). C, D RNA immunoprecipitation of ELAVL1 in HASMCs. CDKN1A RT-PCR harvest determined by agarose gel electrophoresis, and relative immunoprecipitated (IP)/input ratios are shown (n = 3, p < 0.0001; Student t test). E, F RNA pull-down assay using hsa_circ_0000280 probe in vitro. Antisense RNA of hsa_circ_0000280 was negative control (NC). Harvested CDKN1A RT-PCR was determined by agarose gel electrophoresis, and relative immunoprecipitated (IP)/input ratios are shown (n = 3, p < 0.0001; Student t tests). G Prediction of RNA–protein interaction between hsa_circ_0000280 with ELAVL1 using catRAPID algorithm. H Secondary structure prediction of hsa_circ_0000280 using Vienna RNA Web Services. The blue circle shows predicted top three binding sites of hsa_circ_0000280 for ELAVL1. I RIP of ELAVL1 from empty vector (E.vector), circ_280, and three circ-deleted groups. Bound hsa_circ_0000280 was determined by qPCR (n = 5, p < 0.01; Student t tests). Data are presented as means ± SD