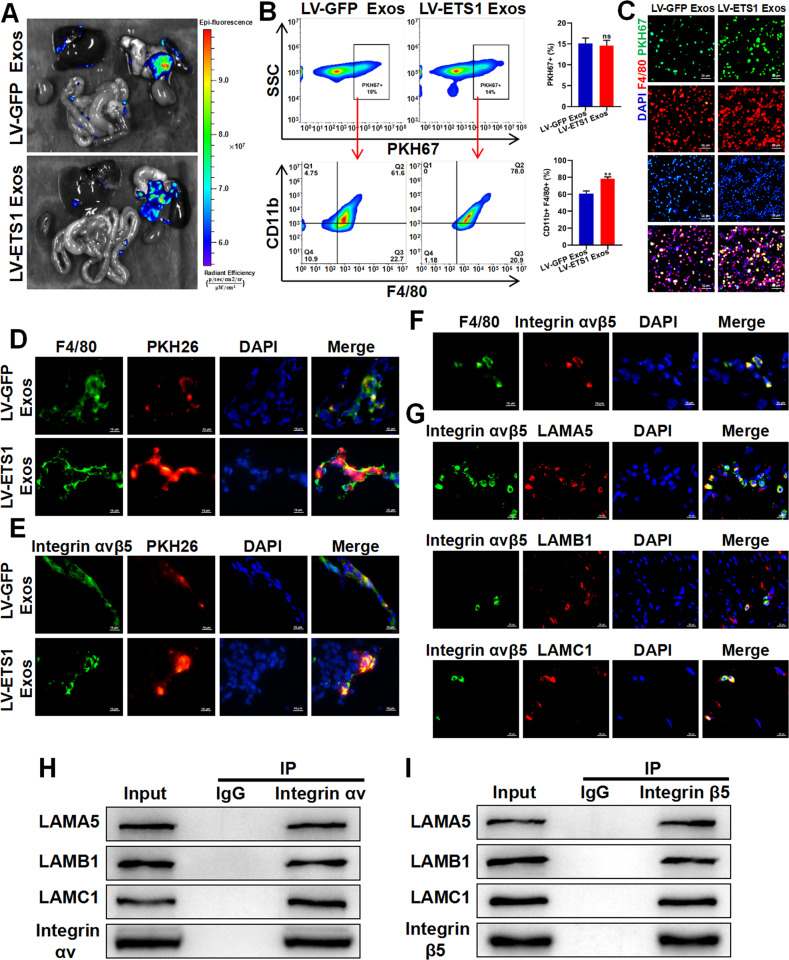
Fig. 4. ETS1 promotes ovarian cancer exosomes uptake by omental macrophages.
A Ex vivo bioluminescence analysis showing uptake of ovarian cancer exosomes by abdominal organs. B, C Flow cytometry analysis (B) and fluorescence microscope observation (C) showing uptake of PKH67-labeled LV-ETS1 Exos and LV-GFP Exos by omental macrophages. Scale bars: 20 μm at ×200 magnification. D Immunofluorescence analysis showing PKH26-labeled LV-ETS1 Exos and LV-GFP Exos (red), F4/80 (green), and DAPI (blue) staining in nude mice omentum. Scale bars: 10 μm at ×630 magnification. E Immunofluorescence analysis showing PKH26-labeled LV-ETS1 Exos and LV-GFP Exos (red), integrin αvβ5 (green) and DAPI (blue) staining in nude mice omentum. Scale bars: 10 μm at ×630 magnification. F Immunofluorescence analysis showing F4/80 (green), integrin αvβ5 (red) and DAPI (blue) staining in nude mice omentum. Scale bars: 10 μm at ×630 magnification. G Immunofluorescence analysis showed LAMA5, LAMB1 and LAMC1 (red) colocalized with integrin αvβ5 (green) in nude mice omentum. Scale bars: 10 μm at ×630 magnification. H, I Co-IP analysis showed LAMA5, LAMB1 and LAMC1 could interact with integrin αv (H) and integrin β5 (I) protein in RAW 264.7 cells. Data are shown as mean ± SD. **P < 0.01, ns non-significant.