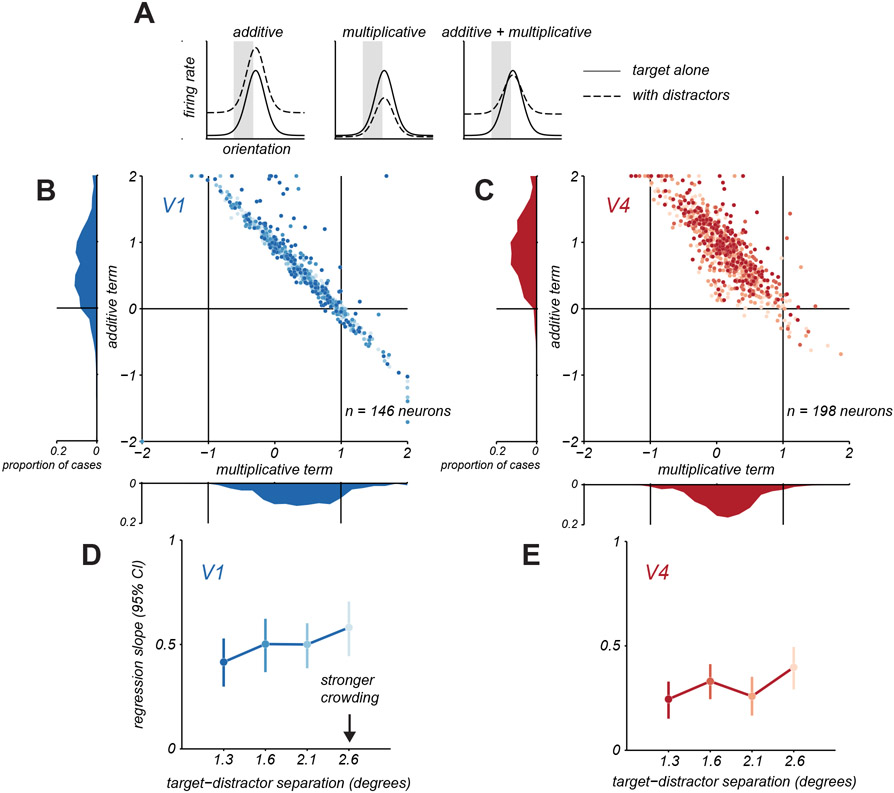
Figure 5. Additive and multiplicative changes in target tuning with distractors.
A. Schematic illustration of how target tuning amid distractors (dashed line) might involve additive translation, multiplicative scaling, or combined changes in target only tuning (solid line). B. Multiplicative and additive terms fit to V1 neurons under crowding. Each point represents one neuron and distractor spacing condition, darker shades indicate closer distractor spacing. Marginal distributions of parameters are shown along the axes. C. Same as in B, but for V4 neurons. D. Change in V1 discriminability as a function of target-distractor spacing by applying the additive and multiplicative changes in target only tuning from B. Change in discriminability was quantified using the slope of the regression line relating discriminability for target only and target with distractors conditions. Error bars indicate 95% confidence interval. E. Same as in D, but for V4. See also Figures S5 and S7.