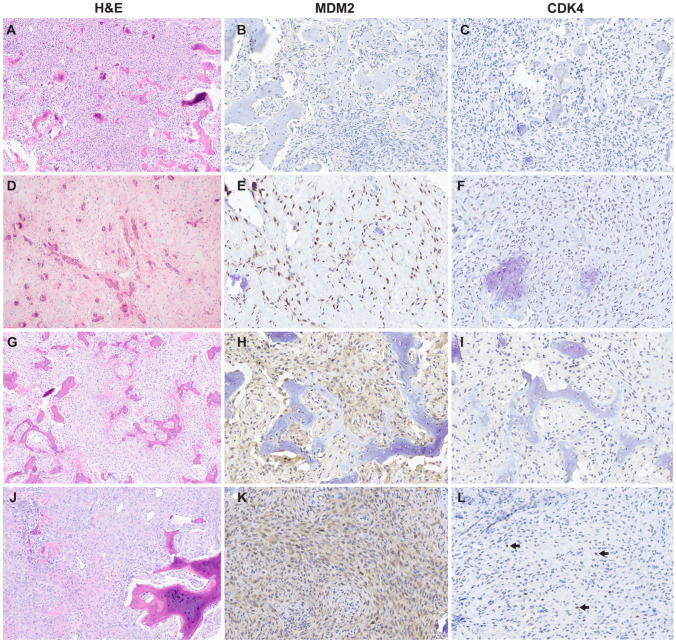
Fig. 1.
Representative histomorphology and immunohistochemistry results of ossifying fibroma. A–C Ossifying fibroma (case 9) composed of low-grade cellular fibroblastic stroma that invades and replaces woven bone and forms new bone; no nuclear immunoreactivity MDM2 or CDK4. D–F Juvenile psammomatoid ossifying fibroma (case 11) with hyalinized stroma and bone deposits with concentric calcification; nuclear MDM2 positivity in > 26–50% of spindle cells; no nuclear immunoreactivity to CDK4. G–I Juvenile trabecular ossifying fibroma (case 26) with cellular spindled growth and woven bone that presents as anastomosing trabeculae with mineralization; nuclear MDM2 positivity in ≤ 10% of cells (nuclear staining in osteoclast-type giant cells was disregarded- see methods).; no nuclear immunoreactivity to CDK4. J–L Ossifying fibroma (case 41) with bone formation and dense cellular stroma with mineralization and osteoclast-type giant cells; strong cytoplasmic and rare MDM2 nuclear staining in spindle cells; rare faint nuclear CDK4 staining in spindle cells (arrows highlight rare positive nuclei)