Fig. 8. Hypothesis for neural mechanisms of RMTg GABAergic neurons suppressing REM sleep through the LDT/LH.
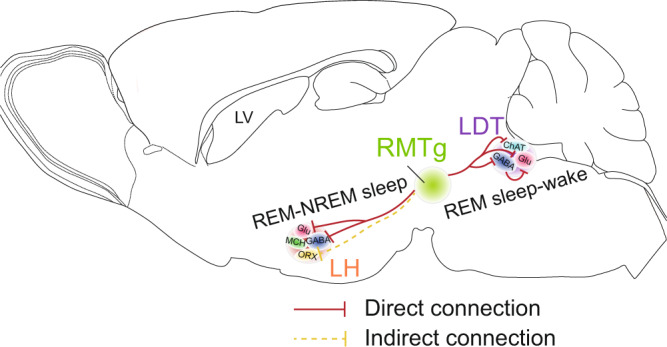
RMTg GABAergic neurons inhibited cholinergic and/or GABAergic neurons in the LDT to cease REM sleep. Activation of RMTg GABAergic neurons inhibited GABAergic interneurons in the LDT, which then disinhibited glutamatergic neurons in the LDT to facilitate REM sleep–wake transitions. Activation of RMTg GABAergic terminals in the LH facilitated REM–NREM sleep transitions through direct inhibition of glutamatergic and/or GABAergic neurons and/or through indirect synaptic connection with orexin neurons. RMTg rostromedial tegmental nucleus, LDT laterodorsal tegmentum, LH lateral hypothalamus, LV lateral ventricle, ChAT cholinergic neurons, Glu glutamatergic neurons, ORX orexin neurons, MCH melanin-concentrating hormone neurons.
