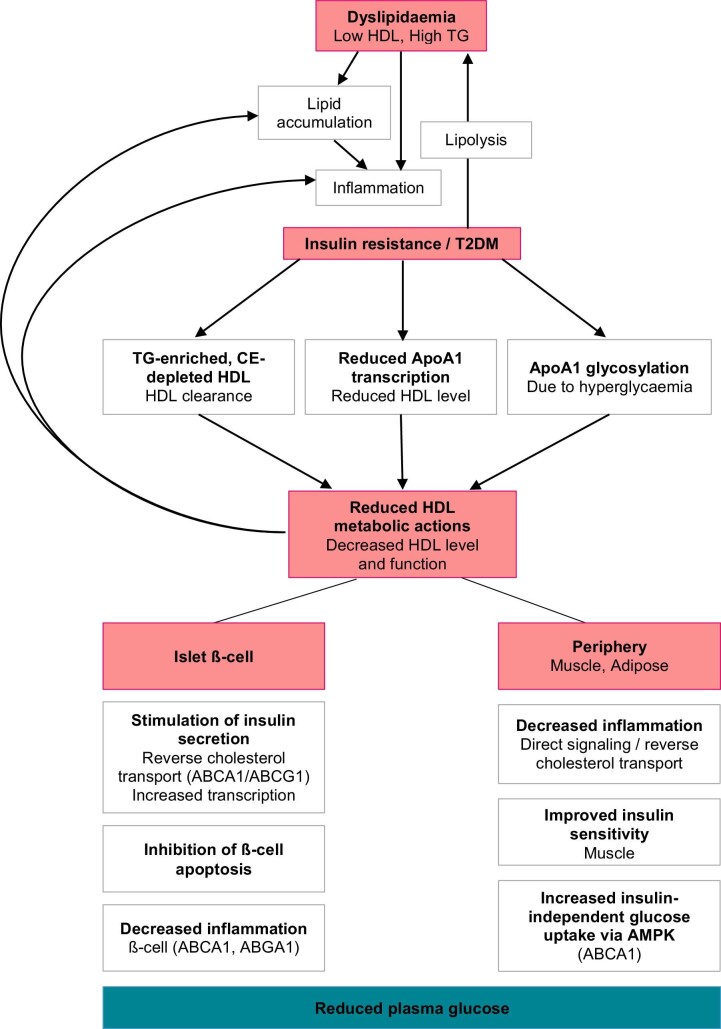
Figure 1.
Mechanisms linking HDL-C and diabetes. Dyslipidaemia (low HDL) causes lipid accumulation and inflammation propagating insulin resistance and T2DM. T2DM increases ApoA1 glycation, reduces ApoA1 transcription and changes HDL composition to increase clearance, reducing HDL level and function. HDL normally has reverse cholesterol transport and anti-inflammatory actions at ß-cells and in periphery that decrease plasma glucose.7 HDL promotes insulin secretion via ApoA130 and ABCA1/ABCG (1) or through stimulating insulin transcription. HDL-C may inhibit ER-stress-induced ß-cell apoptosis31 and islet cell inflammation via ABCA1 and ABCG.32 Loss of HDL particles and function exacerbates lipid accumulation and inflammation and increases plasma glucose, contributing to a vicious cycle.