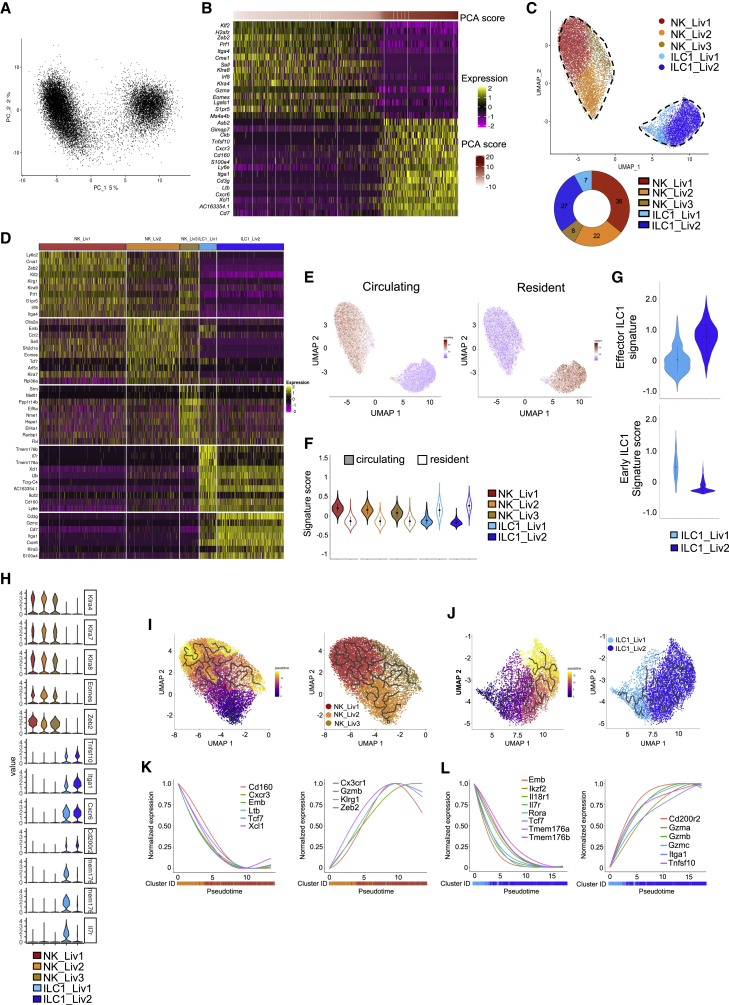
Figure 2.
Different transcriptional features between hepatic NK cell and ILC1 populations
(A) Principal-component analysis (PCA) of 16,262 hepatic NKp46+NK1.1+ cells.
(B) Heatmap showing the top 15 genes with the lowest or highest PC1 scores, ranked according to their score values. Cells and genes are sorted by principal-component scores.
(C) UMAP projection of hepatic NKp46+NK1.1+ cells clustered according to RNA levels. The donut graph shows the percentage of each liver NKp46+NK1.1+ subset identified.
(D) Heatmap of the top 10 upregulated DEGs of the identified NKp46+NK1.1+ clusters, ranked by adjusted p value (FC > 0.35 and p < 0.05).
(E) UMAP plot overlaid with tissue-resident and circulating lymphocyte signatures.
(F) Module score analysis for tissue-resident and circulating lymphocyte signatures for clusters identified in (C) (mean ± SD).
(G) Module score analysis of “early” and "effector" ILC1 transcriptomic signatures for the hepatic ILC1 subsets identified in (C) (mean ± SD).
(H) Violin plots showing mRNA expression profiles of selected genes across Seurat clusters.
(I and J) Left panel: pseudotime analysis of cells included in NK (I) and ILC1 (J) clusters. UMAPs are colored according to pseudotime scores (left) and cell clusters (right).
(K and L) Normalized expression of genes along the pseudotime axis calculated for the cells included in NK (K) and ILC1 (L) clusters. Color bars indicate cluster identity.