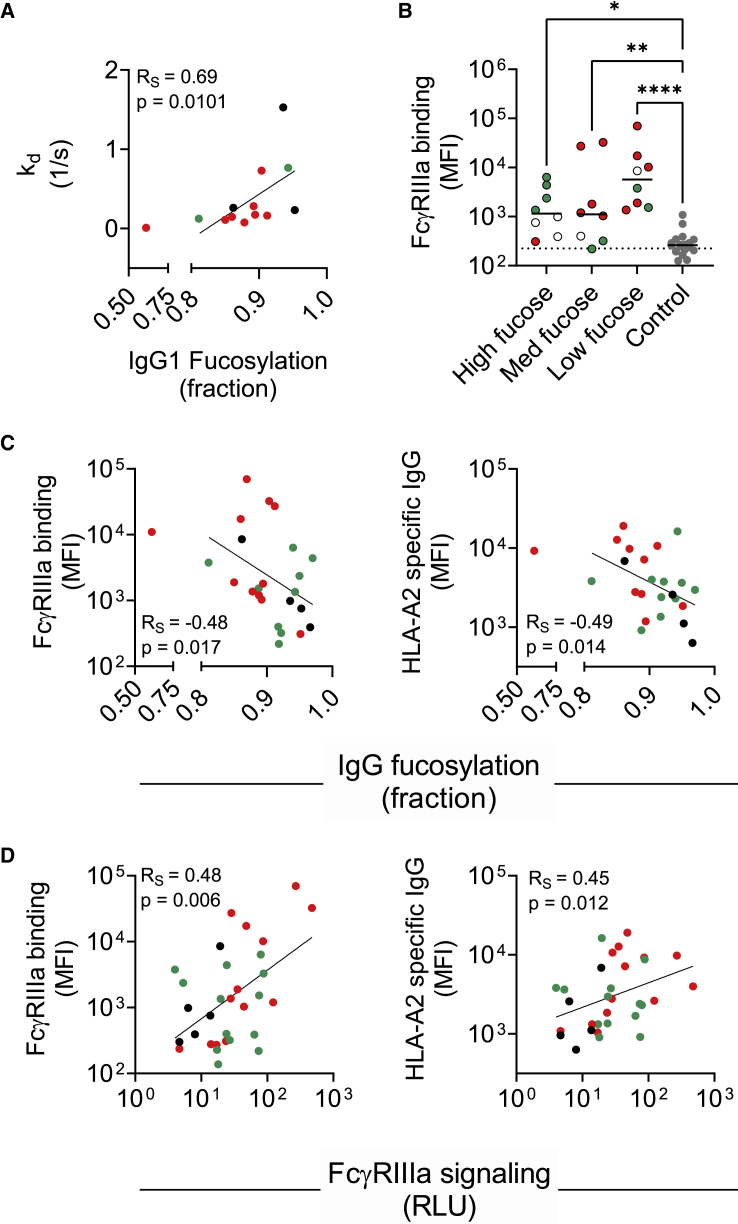
Figure 4.
Associations of serum-derived HLA-A2-specific antibody fucosylation with FcγRIIIa binding and signaling
(A) Spearman’s correlation (RS) between IgG1 fucosylation and FcγRIIIa dissociation rate (n = 13).
(B) FcγRIIIa binding characterization in high (n = 8), medium (n = 8), and low (n = 8) fucose samples and negative controls (n = 18). Serum samples were tested at a 1:500 serum dilution. Statistical analysis was performed using ordinary one-way ANOVA adjusted for multiple comparisons using Tukey’s test. Solid lines indicate group median. Data shown are representative of two technical replicates.
(C and D) Spearman’s correlations between IgG1 fucosylation (n = 24) (C) and FcγRIIIa signaling (n = 31) (D) with FcγRIIIa binding (left) and HLA-A2-specific IgG levels (mean fluorescence intensity [MFI]) (right). Patients with AMR (red), patients without AMR (green), and patients with no AMR information (black) are indicated in color.