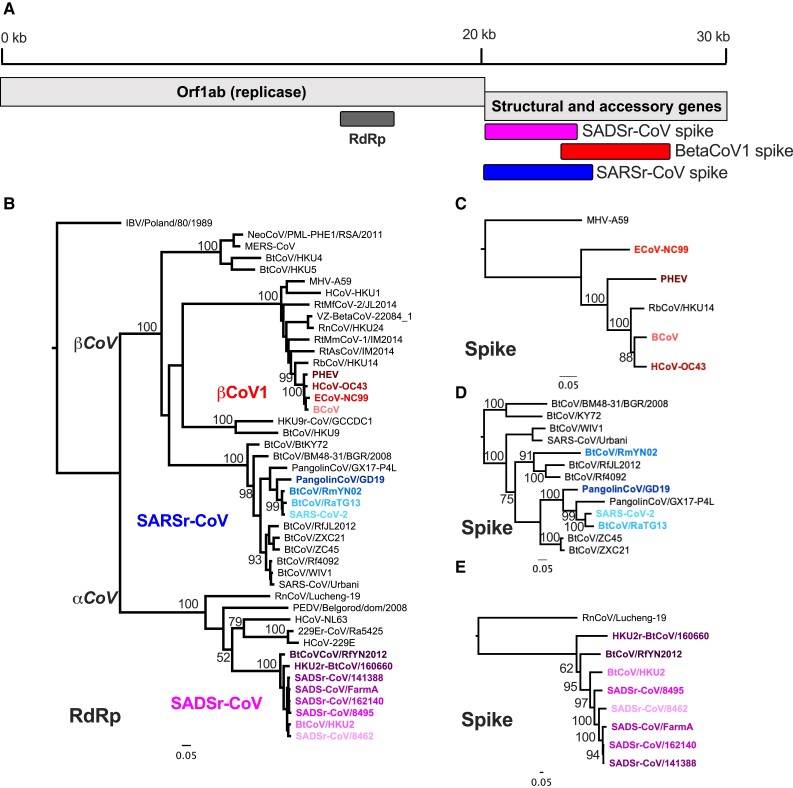
Fig. 1.
AlphaCoV and BetaCoV phylogenetic relationships are genome region-dependent. (A) Basic coronavirus genome organization with the 5′ ∼20 kb comprising the replicase gene that is proteolytically processed into up to 16 individual proteins. The 3′ 10 kb comprises structural and genus-specific accessory genes. (B) Maximum-likelihood (ML) phylogenetic tree of alpha and betaCoVs full-length RNA-dependent RNA-polymerase encoding region of Orf1ab. (C) ML phylogenetic tree of full-length spike genes from viruses in the species Betacoronavirus 1 (red) rooted with the distantly related betacoronavirus mouse hepatitis virus. (D) ML phylogenetic tree of spike genes of SARSr-CoVs, with SARS-CoV-2-like viruses further analyzed in the paper highlighted in blue. (E) ML phylogenetic tree of spike genes from SADSr-CoVs (magenta) rooted with the distantly related alphacoronavirus RnCov/Lucheng-19.