| Two-Parameter Isotherm |
| Langmuir |
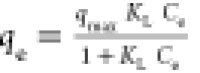 qmax is a parameter
that reflects monolayer formation, KL is
the adsorption equilibrium constant qmax is a parameter
that reflects monolayer formation, KL is
the adsorption equilibrium constant |
qmax (mg/g) |
322 |
0.98 |
|
KL (L/mg) |
1.80 × 10–3
|
| Freundlich |
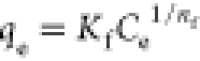 Kf is a constant
for the relative adsorption capacity, 1/nf is a constant indicative of surface heterogeneity Kf is a constant
for the relative adsorption capacity, 1/nf is a constant indicative of surface heterogeneity |
Kf (L/g) |
1.9 |
0.97 |
| 1/nf (−) |
0.71 |
| D-R |
qe = (qm) exp. (−Kad ε2) ε = RT (1 + (1/Ce)) Kad is a constant related
to adsorption energy, qm is the theoretical
adsorption capacity. |
qm (mg/g) |
231 |
0.99 |
|
Kad (mol2/kJ2) |
0.036 |
| Three-Parameter Isotherm |
| Langmuir–Freundlich |
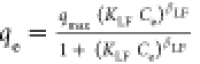 qmax, KLF and βLF are the max. adsorption
capacity, the equilibrium constant, and the heterogeneity parameter,
respectively. qmax, KLF and βLF are the max. adsorption
capacity, the equilibrium constant, and the heterogeneity parameter,
respectively. |
qmax (mg/g) |
199 |
0.99 |
|
KLF (L/mg) |
0.5 ×
10–2
|
| βLF (−) |
1.84 |
| Sips |
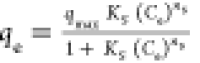 qmax, KS and ns are the
Sips max. adsorption capacity, equilibrium constant, and the model
exponent, respectively qmax, KS and ns are the
Sips max. adsorption capacity, equilibrium constant, and the model
exponent, respectively |
qmax (mg/g) |
196 |
0.99 |
|
Ks (L/mg) |
4.90 × 10–5
|
|
ns (−) |
1.84 |
| Redlich–Peterson |
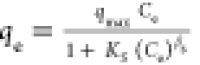 qmax, Ks and βs are the isotherm constants qmax, Ks and βs are the isotherm constants |
qmax (L/mg) |
0.47 |
0.99 |
|
Ks (mg/g)g
|
7.8 × 10–7
|
| βs (−) |
2.12 |
| Toth |
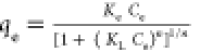 Ke, Kl, and n are Tóth max.
adsorption capacity, Tóth equilibrium constant, and Tóth
model exponent, respectively Ke, Kl, and n are Tóth max.
adsorption capacity, Tóth equilibrium constant, and Tóth
model exponent, respectively |
Ke (mol*L/mg*mg) |
0.86 |
0.99 |
|
KL (L/mg) |
6.90 ×
10–6
|
|
n (−) |
1.79 |
| Four-Parameter Isotherm |
| Baudu |
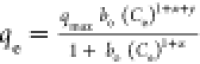 qmax and bo are the Baudu max. adsorption capacity and
the equilibrium constant, respectively, x and y are the Baudu parameters qmax and bo are the Baudu max. adsorption capacity and
the equilibrium constant, respectively, x and y are the Baudu parameters |
qmax (mg/g) |
171 |
0.99 |
|
bo (−) |
5.17
× 10–5
|
|
X (−) |
19.7 × 10–3
|
|
Y (−) |
8.45
× 10–1
|
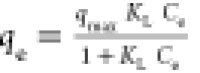 qmax is a parameter
that reflects monolayer formation, KL is
the adsorption equilibrium constant
qmax is a parameter
that reflects monolayer formation, KL is
the adsorption equilibrium constant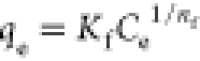 Kf is a constant
for the relative adsorption capacity, 1/nf is a constant indicative of surface heterogeneity
Kf is a constant
for the relative adsorption capacity, 1/nf is a constant indicative of surface heterogeneity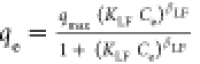 qmax, KLF and βLF are the max. adsorption
capacity, the equilibrium constant, and the heterogeneity parameter,
respectively.
qmax, KLF and βLF are the max. adsorption
capacity, the equilibrium constant, and the heterogeneity parameter,
respectively.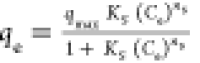 qmax, KS and ns are the
Sips max. adsorption capacity, equilibrium constant, and the model
exponent, respectively
qmax, KS and ns are the
Sips max. adsorption capacity, equilibrium constant, and the model
exponent, respectively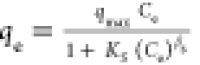 qmax, Ks and βs are the isotherm constants
qmax, Ks and βs are the isotherm constants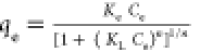 Ke, Kl, and n are Tóth max.
adsorption capacity, Tóth equilibrium constant, and Tóth
model exponent, respectively
Ke, Kl, and n are Tóth max.
adsorption capacity, Tóth equilibrium constant, and Tóth
model exponent, respectively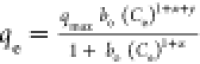 qmax and bo are the Baudu max. adsorption capacity and
the equilibrium constant, respectively, x and y are the Baudu parameters
qmax and bo are the Baudu max. adsorption capacity and
the equilibrium constant, respectively, x and y are the Baudu parameters