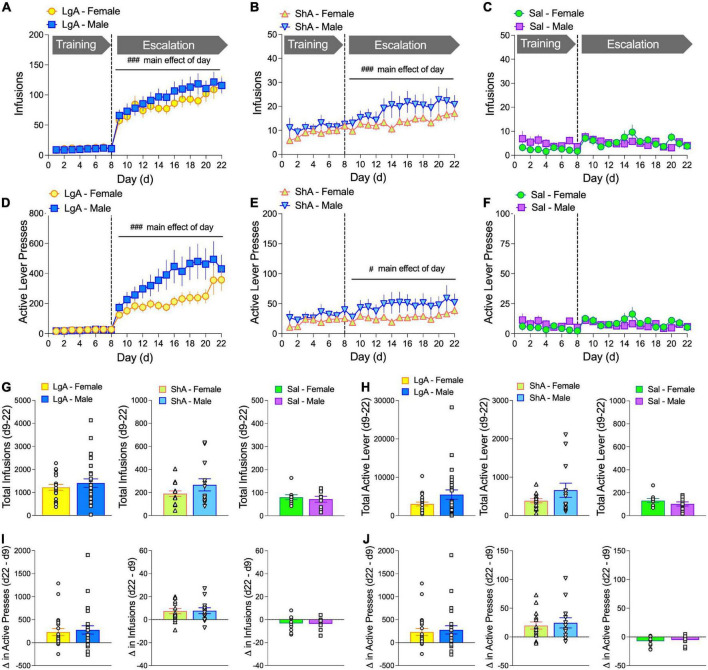
FIGURE 2.
Female and male rats escalate oxycodone self-administration under both long access (LgA, 6 h) and short access (ShA, 1 h) conditions. Oxycodone self-administration behavior is shown as # of infusions/day (A–C) and # of active lever presses/day (D–F) for male and female rats across the 22 days of the self-administration paradigm. Groups included rats that self-administered oxycodone under LgA conditions (A,D) or under ShA conditions (B,E) during the escalation phase (days 9–22) and rats that self-administered saline (C,F). Under both LgA and ShA, but not saline, conditions, there was a main effect of Day. There were no sex differences in total infusions (G) or active lever presses (H) during the escalation phase (d9–22). There were no sex differences in the change in number of infusions (I) or active lever presses (J) from escalation day 9 to escalation day 22, although the net change for LgA and ShA, but not saline, rats was >0, indicating escalation of intake (see Supplementary Figure 2). #p < 0.05, ###p < 0.001, main effect of Day. N: LgA (22 females, 26 males); ShA (15 females, 13 males); Sal (10 females, 9 males).