TABLE 4.
Main components present in cinnamon and their mechanisms of action.
| Cinnamon oil | Structure | Molecular formula | Effect | Mechanism |
|---|---|---|---|---|
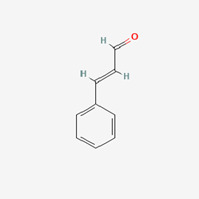
| Cinnamaldehyde |
|
C9H8O https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/Cinnamaldehyde | Anti- lipidemic and anti-hyperglycemic | 1. Improvement in enzyme activity, including those directly engaged in glucose metabolism and those involved in excretion (Stevens and Allred, 2022) |
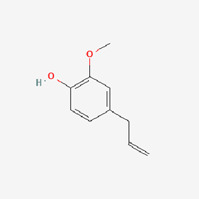
| Eugenol |
|
C10H12O2 https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/Eugenol | Anti-hyperglycemic, antioxidant, antibacterial, and anti-inflammatory | 2. Altering ghrelin secretion and their effects on food intake and gastric emptying (Anand et al., 2010) |
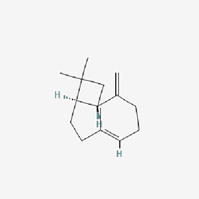
| Beta-caryophyllene |
|
C15H24 https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/beta-Caryophyllene | Anti-hyperglycemic antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and anti-lipidemic | 3. Providing sympathetic actions; increased noradrenaline and thermogenic action (Saito et al., 2015) |
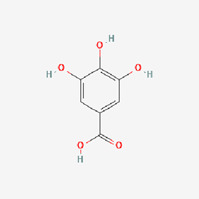
| Gallic acid |
|
C7H6O5 https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/Gallic-acid | Antioxidant, antimicrobial, anti-inflammatory, and anticancer (Fernandes and Salgado, 2016) | 4. Boosting insulin sensitivity through increasing insulin receptor mRNA and protein expression (IR) (Mani et al., 2021) |
| 5. Enhancing the expression of proteins involved in glucose transport (Stevens and Allred, 2022) | ||||
| 6. Acting as a-glycosidase inhibitors (Singh et al., 2016) | ||||
| 7. Protecting β-cells by alleviating hyperglycemia (Basha and Sankaranarayanan, 2016) |
