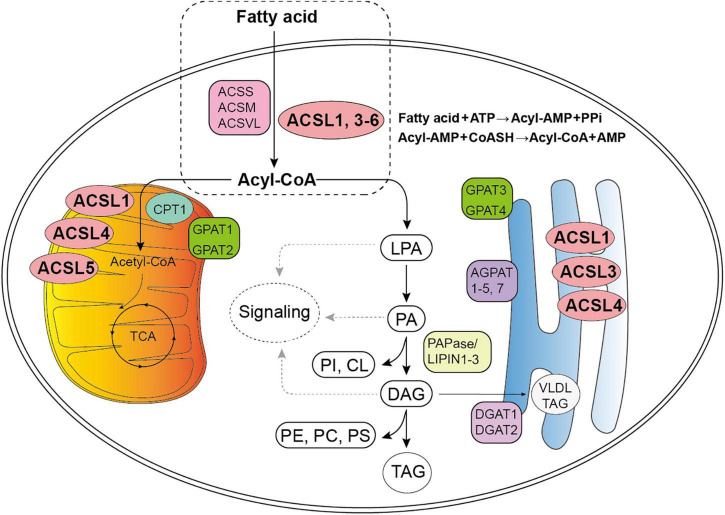
FIGURE 1.
Diagram for fatty acid (FA) metabolism. The first stage of FA metabolism is the activation of FA, which requires a two-step reaction catalyzed by Acyl-CoA synthetases: an acyl-AMP intermediate is first formed from ATP, and then exchanged with CoA to yield the activated acyl-CoA. (Gassler et al., 2007; Soupene and Kuypers, 2008; Golej et al., 2011; Nakahara et al., 2012; Rossi Sebastiano and Konstantinidou, 2019). Subsequently, Acyl-CoA participates in the synthesis of lysophosphatidic acid (LPA), phosphatidic acid (PA), glycerol diester (DAG), and triacylglycerol (TAG) (Coleman, 2019). Acyl-CoAs can also be converted to acyl-carnitines by carnitine palmitoyltransferase (CPT1) to enter the mitochondria for β-oxidation and tricarboxylic acid cycle (TCA). The LPA, PA, and DAG intermediates may initiate signaling cascades, and PA and DAG are also precursors of all the glycerophospholipids: phosphatidylinositol (PI), phosphatidylcholine (PC), phosphatidylethanolamine (PE), phosphatidylserine (PS), and cardiolipin (CL) (Coleman, 2019). The TAG may remain in the cytosol within a lipid droplet or, in liver, be secreted a part of a very-low-density lipoprotein particle (VLDL) (Coleman, 2019). ACSS, short–chain acyl–CoA synthetase; ACSM, medium–chain acyl–CoA synthetase; ACSL, long–chain acyl–CoA synthetase; ACSVL, very long–chain acyl–CoA synthetase; AMP, adenosine monophosphate; PPi, pyrophosphoric acid; CoASH, coenzyme A; GPAT, glycerol-3-P acyltransferases; AGPAT, 1-acylglycerol-3-phosphate acyltransferases (also known as LPA acyltransferase); PAPase/Lipin, PA hosphohydrolases; DGAT, diacylglycerol acyltransferases.