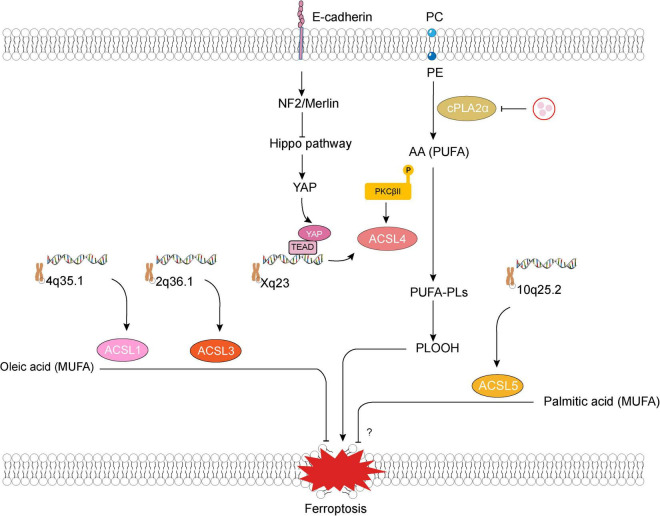
FIGURE 2.
Long-chain acyl-coenzyme A synthetases family member 1, 3–5 (ACSL1, 3–5) and ferroptosis. E-cadherin–NF2–Hippo–YAP pathway suppresses ferroptosis by attenuating YAP-mediated transcription and translation of ACSL4. Lipogenesis involving production of phospholipids containing polyunsaturated fatty acid chains (PUFA-PLs) that are mediated by ACSL4 and multiple other enzymes is required for phospholipid peroxidation and ferroptosis (Jiang et al., 2021). Some pathological states (such as cerebral ischemia) would lead to an unexpected increase in thrombin within neurons, promote the mobilization of phosphatidylcholine (PC) and phosphatidylethanolamine (PE) in the phospholipid membrane of neuronal cells through cytosolic phospholipase A2alpha (cPLA2α), and accelerate the production of polyunsaturated fatty acid, such as arachidonic acid (AA) (Tuo et al., 2022). Besides, ferroptosis inducers promote a slight accumulation of lipid peroxide, which induces the activation of protein kinase C βII (PKCβII). Subsequently, activated PKCβII interacts directly with and phosphorylates ACSL4 at Thr328, which activates ACSL4, triggering the biosynthesis of PUFA-containing lipids and then promoting the generation of lipid-peroxidation products (Zhang H. L. et al., 2022). NF2, neurofibromin 2; YAP, Yes-associated protein; PLOOH, phospholipid hydroperoxide.