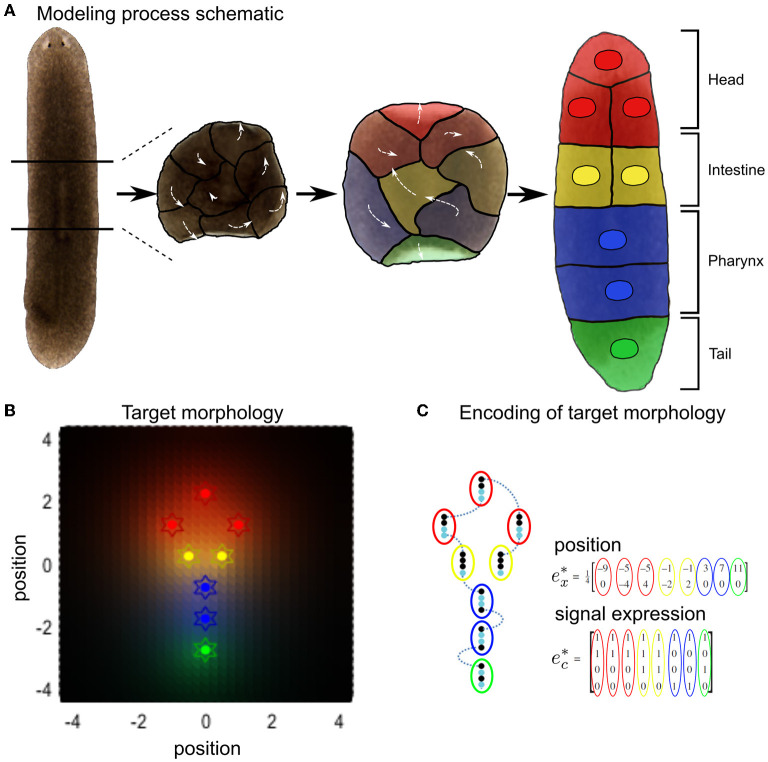
Figure 2.
Schematic of variational Bayesian simulation of simple body shape morphogenesis illustrated by the example of regenerative patterning observed in planarian flatworms. (A) When dissecting out the center piece of a planarian flatworm, the constituent cells will remodel into a whole new worm with normal body axis. For the purpose of illustrating our simulation and for simplicity, cells that form different tissue types were grouped together as one cell. (B) Expected Signal concentrations (background color hues) at each target final position (colored stars) in the target morphology encode the cellular model of inference, with the same color encoding cell type from (A). (C) The target morphology for the arrangement of cells is encoded by expectations of external signals for any given position in the defined target morphology that constitutes the final configuration of cells. Each row in corresponds to a different signaling type, while every column represents the signal expression states for a different cell. Adapted from Kuchling et al. (2020).