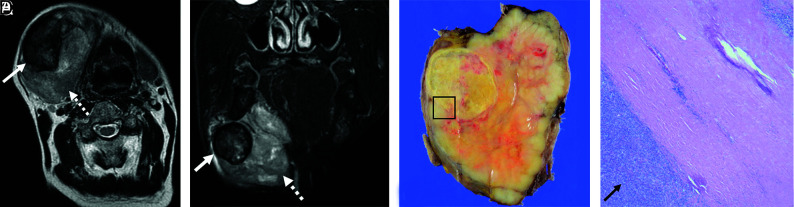
FIG 4.
MR imaging–pathology correlation: invasive type. Invasive CXPA (undifferentiated carcinoma, large-cell type) of the right submandibular gland in a 72-year-old man. A huge mass replaced the right submandibular gland. MRI shows heterogeneous high intensity on T2WI and FS-T2WI (A and B, dotted arrows). Encapsulated nodules with thick low-intensity rims are present inside the tumor on axial T2WI and FS-T2WI (A and B, solid arrows). Macroscopic findings show a solid and white-yellow tumor with nodules in the nodule pattern. The nodule within the tumor corresponds to a black ring sign on MRI (C). Photomicrograph shows ductal and myoepithelial cells with atypical hyperchromatic nuclei (D, H&E, original magnification ×20). The malignant component invaded beyond the capsule (D, arrows) and infiltrated the surrounding fatty tissue. Most nodules within the tumor showed extensive hyalinization/fibrosis with myxoid stroma (D), and the black ring sign matched the hyalinization/fibrosis. The corona sign on FS-T2WI and CE-FS-T1WI reflects pathologically extracapsular tumor cells and/or inflammatory cells.